
Life-Changing EECP Treatment for Refractory Angina: The Non-Invasive Solution When Surgery Fails
EECP Treatment for Refractory Angina: When conventional treatments fall short and chest pain continues to limit your daily activities, hope isn’t lost. Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) emerges as a revolutionary non-invasive therapy specifically designed for patients with refractory angina who have exhausted traditional treatment options.This breakthrough treatment offers new possibilities for individuals facing persistent chest pain despite optimal medical therapy and unsuccessful revascularization attempts. Thousands of patients worldwide have discovered renewed quality of life through this FDA-approved therapy that works by naturally enhancing blood flow to the heart.
Understanding how EECP transforms the lives of refractory angina patients can help you make informed decisions about your cardiac care journey. This comprehensive guide explores the science, benefits, and clinical outcomes of this life-changing treatment approach.
Global Statistics: The Growing Challenge of Refractory Angina
Refractory angina statistics reveal a significant healthcare challenge affecting millions worldwide. Nearly 1,000,000 people in the U.S. alone have refractory angina and 25,000 – 75,000 new cases are diagnosed every year. Globally, the prevalence of refractory angina is more than two million people and is significantly rising.
The condition affects approximately 5-10% of patients with stable coronary artery disease who cannot achieve adequate symptom control through conventional treatments. This translates to hundreds of thousands of individuals living with debilitating chest pain that severely impacts their quality of life.
Healthcare systems face mounting pressure as refractory angina patients consume disproportionate resources. These individuals typically experience:
- Frequent emergency department visits due to uncontrolled symptoms
- Multiple hospitalizations for chest pain evaluation
- Reduced workforce participation leading to economic losses
- Increased healthcare costs averaging 3-4 times higher than stable angina patients
- Psychological distress including depression and anxiety disorders
The long-term impact extends beyond individual suffering. Family members often become caregivers, affecting their professional and personal lives. Social isolation increases as patients avoid activities that trigger symptoms, leading to diminished social connections and support systems.
Without effective intervention, refractory angina patients face progressive functional decline. Many become increasingly dependent on pain medications, potentially leading to addiction issues. The condition significantly reduces life expectancy and quality of life, making innovative treatments like EECP therapy crucial for patient outcomes.
Clinical Pathways and Pathogenesis of Refractory Angina
Understanding Refractory Angina Development
Refractory angina pathogenesis involves complex mechanisms that make conventional treatments ineffective. The condition develops when coronary arteries cannot deliver adequate blood flow to meet myocardial oxygen demands, despite optimal medical therapy and unsuccessful revascularization attempts.
Microvascular Dysfunction plays a central role in refractory angina development. Small coronary vessels lose their ability to dilate appropriately during increased oxygen demand. This dysfunction often results from:
- Endothelial dysfunction reducing nitric oxide production
- Inflammatory processes affecting vessel wall integrity
- Metabolic disorders including diabetes and insulin resistance
- Oxidative stress damaging cellular structures
Macrovascular Disease contributes through severe coronary stenosis that cannot be adequately addressed through surgical or percutaneous interventions. Patients may have:
- Diffuse coronary disease involving multiple vessel segments
- Chronic total occlusions resistant to recanalization
- Small vessel disease unsuitable for stenting
- Previous failed interventions with restenosis or graft failure
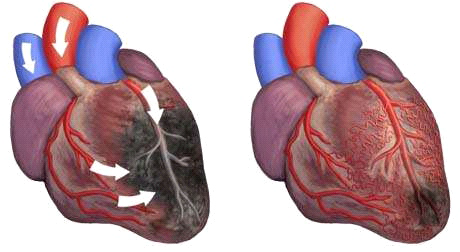
Disease Progression Pathways
Stage 1 – Incomplete Revascularization: Initial treatments provide partial relief, but residual ischemia persists. Patients experience reduced but persistent anginal symptoms despite technically successful procedures.
Stage 2 – Treatment Resistance: Standard antianginal medications fail to provide adequate symptom control. Patients require increasing medication doses or combinations without achieving satisfactory relief.
Stage 3 – Functional Limitation: Daily activities become severely restricted due to predictable chest pain with minimal exertion. Quality of life deteriorates significantly, affecting employment and social functioning.
Stage 4 – Refractory State: Complete exhaustion of conventional treatment options. Patients experience frequent symptoms despite maximal medical therapy, making them candidates for alternative treatments like EECP.
Molecular Mechanisms
Ischemic Cascade: Inadequate oxygen delivery triggers cellular changes including ATP depletion, lactate accumulation, and membrane instability. These changes cause the characteristic chest pain and functional limitations.
Inflammatory Response: Chronic ischemia promotes inflammatory cytokine release, further compromising coronary function. This creates a vicious cycle of ongoing arterial dysfunction and symptom progression.
Neurogenic Factors: Persistent ischemia alters cardiac pain perception, potentially leading to hypersensitivity. Some patients develop heightened pain responses even to minimal ischemic stimuli.
EECP Treatment for Refractory Angina: Revolutionary Mechanism
Enhanced External Counterpulsation for refractory angina works through sophisticated physiological mechanisms that address the underlying causes of persistent chest pain. The EECP mechanism of action is similar to that of an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) by administering a vigorous pressure pulse via external blood pressure cuffs during the heart’s relaxation phase.
Primary Therapeutic Mechanisms
Diastolic Augmentation: EECP creates external pressure waves that significantly increase blood flow during diastole when coronary arteries fill with blood. This enhanced perfusion delivers more oxygen and nutrients to ischemic heart muscle, reducing anginal symptoms.
Afterload Reduction: During systole, all cuffs deflate simultaneously, reducing the resistance against which the heart pumps. This mechanism decreases cardiac workload and oxygen consumption, providing symptom relief.
Collateral Circulation Development: Repeated pressure waves stimulate growth factor release, promoting new blood vessel formation. This natural bypass system provides alternative pathways for blood flow around blocked coronary arteries.
Advanced Physiological Effects
Endothelial Function Improvement: EECP treatment enhances nitric oxide production through increased shear stress on arterial walls. Improved endothelial function promotes better vasodilation and reduced arterial stiffness.
Anti-inflammatory Actions: Studies demonstrate significant reductions in inflammatory markers following EECP therapy. Lower inflammation levels support arterial healing and may prevent further disease progression.
Neurological Benefits: Enhanced cerebral perfusion during treatment may improve cognitive function and reduce depression commonly associated with refractory angina.
Metabolic Enhancements: Improved circulation supports better glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with refractory angina.
EECP vs. Alternative Refractory Angina Treatments
| Treatment Option | Invasiveness | Success Rate | Duration of Relief | Safety Profile | Repeat Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EECP Therapy | Non-invasive | 75-85% | 3-5 years | Excellent (<2% complications) | Possible after 2-3 years |
| Transmyocardial Revascularization | Highly invasive | 60-70% | 2-3 years | Moderate (5-10% mortality) | Limited options |
| Spinal Cord Stimulation | Minimally invasive | 70-80% | Variable | Good (3-5% complications) | Device replacement needed |
| Gene/Cell Therapy | Minimally invasive | 40-60% | Unknown | Under investigation | Limited data |
| Cardiac Shock Wave | Non-invasive | 50-70% | 1-2 years | Good | Possible |
| Maximum Medical Therapy | Non-invasive | 30-50% | Ongoing treatment | Variable | Continuous adjustment |
Advantages of EECP Over Alternatives
Superior Safety Profile: EECP is a safe treatment for highly symptomatic patients with refractory angina. Enhanced external counterpulsation appears to be a safe and well-tolerated treatment option in patients with RAP. Complication rates remain below 2%, primarily involving minor skin irritation or muscle discomfort.
Sustained Benefits: EECP offers an effective, durable therapeutic approach for refractory angina. Decreased angina and improvement in quality of life were maintained at 2 years, with many patients experiencing benefits lasting 3-5 years.
Outpatient Convenience: Patients receive treatment in comfortable outpatient settings without hospitalization requirements. The one-hour daily sessions allow normal activity resumption immediately after treatment.
Comprehensive Benefits: Unlike localized interventions, EECP improves circulation throughout the body. Patients often experience enhanced exercise tolerance, improved mood, and better overall cardiovascular health.
Repeatability: The treatment can be safely repeated if symptoms recur after several years, providing long-term management options for chronic conditions.
Who Needs EECP Treatment for Refractory Angina?
Primary Candidate Categories
Post-Surgical Patients with Persistent Symptoms: Individuals who underwent bypass surgery or angioplasty but continue experiencing limiting angina benefit significantly from EECP therapy. These patients often have incomplete revascularization or developed new blockages.
Medically Optimized Patients: Those receiving maximum tolerated doses of antianginal medications without adequate symptom control represent ideal EECP candidates. The treatment provides additional symptom relief beyond pharmaceutical limitations.
High-Risk Surgical Candidates: Patients considered too high-risk for additional invasive procedures due to comorbidities, advanced age, or previous surgical complications find EECP an excellent alternative.
Patients with Diffuse Coronary Disease: Individuals with widespread arterial involvement that cannot be adequately addressed through targeted interventions benefit from EECP’s systemic approach to circulation improvement.
Specific Patient Populations
Diabetic Patients with Refractory Angina: Diabetes often complicates coronary disease management, making conventional treatments less effective. EECP safely improves circulation while supporting glucose metabolism regulation.
Elderly Patients (Age 70+): Advanced age increases surgical risks significantly while reducing treatment options. EECP provides effective symptom relief without age-related contraindications.
Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Heart failure patients with refractory angina face limited treatment options. EECP can safely improve symptoms while potentially enhancing cardiac function.
Women with Microvascular Disease: Female patients often develop refractory angina due to small vessel disease that doesn’t respond well to conventional treatments. EECP’s microcirculatory benefits make it particularly effective for this population.
Clinical Assessment Criteria
Symptom Severity Evaluation: Candidates typically experience Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class III-IV angina despite optimal medical therapy. These patients have significant functional limitations affecting daily activities.
Previous Treatment Failure: Documentation of unsuccessful conventional treatments including maximal medical therapy and consideration for or failure of revascularization procedures.
Objective Evidence of Ischemia: Stress testing or imaging studies demonstrating ongoing myocardial ischemia despite treatment attempts.
Quality of Life Impact: Significant reduction in functional capacity, employment ability, or social functioning due to persistent anginal symptoms.
The EECP Treatment Protocol for Refractory Angina
Pre-Treatment Assessment
Comprehensive evaluation precedes EECP treatment initiation. Healthcare providers conduct detailed medical history reviews, focusing on previous treatments, current medications, and symptom patterns. Physical examination includes cardiac assessment and evaluation for treatment contraindications.
Diagnostic testing typically involves electrocardiography, echocardiography, and recent stress testing results. Providers assess overall cardiovascular status and optimize medical therapy before beginning EECP treatment.
Patient education plays a crucial role in treatment success. Healthcare providers explain treatment expectations, potential benefits, and the time commitment required for optimal outcomes.
Standard Treatment Protocol
Treatment Duration: The standard protocol involves 35 treatment sessions delivered over 7 weeks with treatments scheduled Monday through Friday. Each session lasts approximately one hour, making the total time commitment manageable for most patients.
Session Structure: Patients lie comfortably on treatment tables with pneumatic cuffs applied to both legs. The system continuously monitors heart rhythm through electrocardiogram leads, ensuring precise pressure timing.
Pressure Parameters: Treatment typically uses 250-300 mmHg pressure applied sequentially from calves to upper thighs. Healthcare providers adjust pressure levels based on patient tolerance and treatment response.
Monitoring Protocol: Continuous cardiac monitoring ensures treatment safety and effectiveness. Providers track blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation throughout each session.
Treatment Progression
Week 1-2: Initial sessions focus on patient comfort and tolerance development. Pressure levels may start lower and gradually increase as patients adapt to treatment sensations.
Week 3-5: Full therapeutic pressure levels are typically achieved. Patients often begin noticing symptom improvements during this phase.
Week 6-7: Final treatment sessions maintain full therapeutic parameters while monitoring for sustained symptom improvement and treatment response.
Post-Treatment Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation occurs after treatment completion, including symptom assessment, functional capacity testing, and quality of life measurements.
Clinical Evidence Supporting EECP for Refractory Angina
International Registry Data
The International EECP Patient Registry provides robust evidence for treatment effectiveness. For patients who have high-risk LV dysfunction, EECP offers an effective, durable therapeutic approach for refractory angina with sustained benefits demonstrated at 2-year follow-up.
Registry data shows 74% of patients experience at least one class improvement in angina severity. Significant improvements occur in exercise tolerance, quality of life measures, and reduced hospitalization rates.
Meta-Analysis Results
Recent systematic reviews demonstrate EECP’s effectiveness across multiple outcome measures. Thirteen outcomes were analyzed … demonstrated a significant clinical advantage in the EECP treatment effectiveness in patients with angina including exercise capacity and ST-segment depression improvements.
Studies consistently show:
- Exercise duration increases averaging 2-3 minutes
- Time to ST-depression improvement during stress testing
- Reduced nitroglycerin consumption by 40-60%
- Improved quality of life scores across multiple domains
Long-term Outcome Studies
The beneficial effects were sustained during a 12-months follow-up period with many patients maintaining improvements for 3-5 years. Long-term studies demonstrate:
- Sustained symptom relief in 70-80% of responders
- Reduced cardiovascular events compared to medically managed controls
- Decreased emergency department visits by 50-70%
- Lower hospitalization rates for cardiac causes
Functional Capacity Improvements
Objective measurements demonstrate significant functional improvements following EECP treatment. Six-minute walk distance increases average 100-150 meters in responders. Exercise stress testing shows improved exercise duration and delayed onset of ST-segment changes.
Quality of life assessments using validated instruments demonstrate significant improvements in physical functioning, emotional well-being, and social activities. These improvements often exceed those achieved through conventional medical therapy alone.
Safety Profile and Contraindications
Excellent Safety Record
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) is a noninvasive treatment that can decrease limiting symptoms in patients with refractory angina pectoris with exceptional safety outcomes. Serious adverse events occur in less than 1% of patients.
Common minor side effects include:
- Mild skin irritation from cuff pressure (10-15% of patients)
- Muscle soreness in legs (5-10% of patients)
- Fatigue during initial treatments (resolving within 1-2 weeks)
- Leg swelling (temporary and mild)
Absolute Contraindications
Severe Aortic Insufficiency: Significant aortic regurgitation can worsen with EECP treatment due to increased diastolic pressure. This condition requires valve repair before considering EECP therapy.
Active Bleeding Disorders: Patients with ongoing bleeding or recent major surgery cannot safely receive EECP treatment. Anticoagulation therapy requires careful evaluation and potential adjustment.
Severe Peripheral Vascular Disease: Ankle-brachial index below 0.4 may contraindicate treatment due to impaired lower extremity circulation. However, mild to moderate peripheral disease doesn’t preclude therapy.
Relative Contraindications
Uncontrolled Hypertension: Blood pressure above 180/110 mmHg requires optimization before treatment initiation. Most patients can safely receive EECP after blood pressure control.
Active Deep Vein Thrombosis: Recent or active clots in leg veins contraindicate treatment until resolution and adequate anticoagulation. Chronic, treated clots may not preclude therapy.
Pregnancy: Limited safety data exists for pregnant patients. The treatment should be deferred until after delivery unless potential benefits clearly outweigh risks.
Severe Heart Failure: Patients with ejection fraction below 20% require careful evaluation. Many heart failure patients can safely receive EECP with appropriate monitoring.
Optimizing EECP Treatment Outcomes
Pre-Treatment Optimization
Medical Therapy Maximization: Ensuring optimal antianginal medications before EECP treatment enhances overall outcomes. This includes appropriate beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and long-acting nitrates at maximum tolerated doses.
Risk Factor Modification: Addressing modifiable cardiovascular risk factors supports treatment success. This includes diabetes control, blood pressure management, and cholesterol optimization.
Lifestyle Preparation: Patients benefit from understanding treatment expectations and preparing for the time commitment. Arranging work schedules and transportation facilitates consistent attendance.
During Treatment Enhancement
Consistent Attendance: Missing treatment sessions can reduce effectiveness. Patients should prioritize attendance and communicate scheduling conflicts early to arrange makeup sessions when possible.
Comfort Optimization: Proper positioning and communication with treatment staff ensures patient comfort throughout sessions. Addressing concerns promptly maintains treatment compliance.
Monitoring Response: Healthcare providers should assess treatment response regularly, adjusting parameters as needed to optimize outcomes while maintaining patient comfort.
Post-Treatment Maintenance
Lifestyle Modifications: Continued heart-healthy lifestyle choices support sustained treatment benefits. This includes regular exercise, proper nutrition, stress management, and smoking cessation.
Medical Follow-up: Regular cardiac care continues after EECP completion. Providers may adjust medications based on symptom improvement and functional capacity enhancement.
Activity Progression: Gradual increase in physical activity capitalizes on improved exercise tolerance. Structured exercise programs can further enhance treatment benefits.
Nutritional Support During EECP Therapy
Heart-Healthy Nutrition Protocol
Anti-inflammatory Diet: Emphasizing foods that reduce systemic inflammation supports EECP treatment effectiveness. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish sources provide cardiovascular protection and may enhance treatment outcomes.
Antioxidant Enhancement: Polyphenol-rich foods including berries, dark leafy greens, and colorful vegetables combat oxidative stress that contributes to coronary disease progression. These nutrients support arterial healing during treatment.
Mediterranean Diet Principles: Following Mediterranean dietary patterns provides comprehensive cardiovascular benefits. This approach emphasizes olive oil, nuts, fish, and plant-based foods while limiting processed foods and red meat.
Specific Nutritional Recommendations
Magnesium Optimization: Adequate magnesium intake supports healthy blood pressure and arterial function. Food sources include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Potassium Balance: Sufficient potassium intake from fruits and vegetables supports healthy blood pressure and cardiac rhythm regulation during treatment.
B-Vitamin Complex: B vitamins, particularly folate and B12, support healthy homocysteine levels. Elevated homocysteine contributes to arterial damage and treatment resistance.
Coenzyme Q10: This nutrient supports cellular energy production and may enhance treatment outcomes. Food sources include organ meats, fish, and nuts, though supplementation may be considered.
Exercise Integration with EECP Treatment
Progressive Exercise Program
Walking Program: Beginning with short, low-intensity walks and gradually increasing duration supports treatment benefits. Start with 10-15 minutes daily and progress based on symptom tolerance.
Resistance Training: Light resistance exercises using bands or light weights support muscle strength and circulation. Focus on major muscle groups with appropriate rest periods.
Flexibility Maintenance: Gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises prevent stiffness and support circulation. Yoga or tai chi provide additional stress reduction benefits.
Exercise Timing Considerations
Pre-Treatment Exercise: Light warm-up activities before EECP sessions may enhance treatment effectiveness. Simple stretching or short walks prepare the circulatory system for treatment.
Post-Treatment Activity: Gentle activity after EECP sessions supports circulation and may enhance treatment benefits. Avoid strenuous exercise immediately after treatment.
Rest Day Activities: On non-treatment days, maintain light physical activity to support overall cardiovascular health and treatment outcomes.
Long-term Management After EECP Treatment
Sustained Benefit Strategies
Regular Follow-up Assessment: Periodic evaluation of symptoms, functional capacity, and quality of life helps track long-term treatment success. Annual assessments provide valuable outcome data.
Medication Adjustments: Many patients require reduced antianginal medications following successful EECP treatment. Healthcare providers should carefully adjust medications based on symptom improvement.
Repeat Treatment Consideration: If symptoms recur after 2-3 years, repeat EECP treatment may be beneficial. The procedure can be safely repeated with similar effectiveness.
Lifestyle Maintenance
Continued Risk Factor Management: Ongoing attention to diabetes control, blood pressure management, and cholesterol optimization supports sustained treatment benefits.
Exercise Program Continuation: Maintaining regular physical activity within symptom tolerance supports long-term cardiovascular health and treatment benefits.
Stress Management: Chronic stress contributes to coronary disease progression. Continued stress reduction techniques support sustained treatment benefits.
Future Directions in EECP Research
Technology Advancement
Portable EECP Devices: Development of home-based treatment systems could increase accessibility and allow maintenance therapy. These devices would require careful safety monitoring and patient selection.
Enhanced Monitoring Systems: Integration of advanced monitoring technologies could optimize treatment parameters in real-time based on individual patient responses.
Combination Therapies: Research explores combining EECP with other treatments like stem cell therapy or growth factor administration to enhance outcomes.
Treatment Protocol Optimization
Personalized Treatment Plans: Future research may identify biomarkers that predict treatment response, allowing customized protocols for individual patients.
Extended Treatment Courses: Studies investigate whether longer treatment courses provide enhanced or more durable benefits for select patient populations.
Maintenance Protocols: Research explores optimal maintenance strategies to prolong treatment benefits, potentially including periodic “booster” sessions.
Expanded Clinical Applications
Prevention Applications: Investigation of EECP for preventing cardiovascular events in high-risk patients without current symptoms shows promise.
Combination with Regenerative Medicine: Research explores combining EECP with stem cell or gene therapy approaches for enhanced cardiovascular repair.
Cognitive Benefits: Studies investigate EECP’s potential benefits for vascular dementia and cognitive decline related to poor circulation.
Clinical Practice Guidelines Integration
Evidence-Based Recommendations
Major cardiovascular societies increasingly recognize EECP as a valuable treatment option for refractory angina. Guidelines emphasize the importance of patient selection and appropriate timing within the treatment continuum.
American College of Cardiology guidelines acknowledge EECP as a reasonable treatment option (Class IIa recommendation) for patients with refractory angina who are not candidates for revascularization.
European Society of Cardiology guidelines similarly recognize EECP’s role in managing patients with limiting angina despite optimal medical therapy and unsuccessful or unsuitable revascularization.
Implementation Considerations
Healthcare Provider Training: Successful EECP programs require properly trained healthcare providers who understand patient selection, treatment protocols, and outcome monitoring.
Quality Assurance Programs: Establishing standardized protocols and outcome tracking ensures consistent treatment quality and patient safety across different treatment centers.
Patient Education Programs: Comprehensive patient education supports treatment compliance and enhances outcomes through proper expectation setting and lifestyle integration.
Conclusion: Transforming Lives Through EECP Treatment
EECP treatment for refractory angina represents a paradigm shift in cardiovascular care, offering hope to patients who have exhausted conventional treatment options. This revolutionary non-invasive therapy provides significant symptom relief, improved quality of life, and enhanced functional capacity without the risks associated with surgical interventions.
The extensive clinical evidence demonstrates EECP’s effectiveness across diverse patient populations, with sustained benefits lasting 3-5 years in most responders. The treatment’s exceptional safety profile makes it suitable for high-risk patients who cannot undergo additional invasive procedures.
Success with EECP therapy requires appropriate patient selection, adherence to established treatment protocols, and integration with comprehensive cardiovascular care. The treatment works best when combined with optimal medical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing cardiac management.
Healthcare providers and patients should consider EECP as a valuable addition to the treatment armamentarium for refractory angina. The therapy offers renewed hope for improved quality of life and functional capacity in patients facing limited alternatives.
The future of EECP therapy continues to evolve with technological advances and expanded research. As our understanding of the treatment mechanisms grows, protocols will become increasingly personalized and effective.
For patients living with the daily burden of refractory angina, EECP treatment offers a path toward restored function, reduced symptoms, and enhanced quality of life. This proven therapy represents hope when traditional treatments have reached their limits.
About the Author
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a distinguished clinical nutritionist and researcher with specialized expertise in EECP therapy and clinical nutrition. As an expert in treating patients with lifestyle disorders, he has successfully treated over 25,000 heart and diabetes patients across the globe.
Mr. Sengar serves as the Founder of FIT MY HEART and works as a Consultant at NEXIN HEALTH and MD CITY Hospital Noida. His extensive experience in cardiovascular care and innovative non-surgical treatment approaches makes him a leading authority in integrated EECP therapy applications combined with holistic healing methods.
His practice focuses on providing comprehensive alternatives to traditional cardiac interventions, helping patients achieve optimal cardiovascular health through evidence-based non-surgical treatments combined with lifestyle optimization and natural healing approaches.
For more information about integrated non-surgical cardiac treatments and comprehensive cardiovascular health services, visit www.viveksengar.in.
💬 Need Expert Guidance for Your Health?
🌿 NexIn Health is India’s Leading Integrated Wellness Center, specializing in:
-
Non-Surgical Heart Disease Treatments
-
Diabetes Reversal Programs
-
Pain Management
-
Obesity & Fatty Liver Management
-
Women’s Hormonal Health (PCOS, Menopause, etc.)
With a team of 25+ wellness coaches, doctors, clinical nutritionists, and researchers, and over 30 centers globally, NexIn Health combines modern science with natural, non-invasive healing methods — empowering patients to reclaim their health without surgery or lifelong medications.
🔗 Visit NexIn Health: www.nexinhealth.in
📞 Call or WhatsApp: +91 9310 14 5010
📩 Email: care@nexinhealth.in
✅ Whether you’re seeking a second opinion or want to reverse your health condition naturally — take the first step towards healing today.
Your health transformation begins with the right expert.
Connect Now. Live Better.
Ayurvedic Heart Blockage Treatment
Revolutionary Non-Surgical Heart Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions:
Que: What is refractory angina?
Ans: Refractory angina is chronic chest pain that persists despite medications, stents, or bypass surgery.
Que: What is EECP treatment for refractory angina?
Ans: EECP (Enhanced External Counter Pulsation) is a non-invasive therapy that increases blood flow to the heart, relieving angina symptoms without surgery.
Que: How does EECP work for angina patients?
Ans: EECP uses air-filled cuffs on the legs to push blood back to the heart during relaxation, improving oxygen delivery to starved heart muscles.
Que: Is EECP a good option when bypass or stenting fails?
Ans: Yes, EECP is especially helpful for patients who continue to have angina despite stents or bypass, or who are not surgical candidates.
Que: How many EECP sessions are needed for angina relief?
Ans: Typically, 35 sessions over 6–7 weeks are required for optimal improvement in angina symptoms.
Que: Does EECP improve exercise tolerance in refractory angina?
Ans: Yes, patients often report increased walking distance, reduced fatigue, and better quality of life.
Que: Is EECP safe for elderly or high-risk patients?
Ans: Yes, EECP is non-invasive and well-tolerated, making it safe even for elderly or frail patients.
Que: Can EECP reduce the need for angina medications?
Ans: Many patients experience symptom relief and may require fewer medications after completing EECP therapy.
Que: Is the effect of EECP therapy long-lasting?
Ans: Yes, benefits can last for several years, especially when supported by healthy lifestyle changes.
Que: Are there any side effects of EECP for angina patients?
Ans: Side effects are minimal, including mild leg soreness or bruising, which typically resolve quickly.
Que: Can EECP treatment be repeated if angina symptoms return?
Ans: Yes, EECP is repeatable and can be done again if symptoms reappear after some time.
Que: Does EECP create new blood vessels in the heart?
Ans: Yes, EECP stimulates the formation of collateral vessels, which act like natural bypasses in the heart.
Que: Who is not eligible for EECP therapy?
Ans: Patients with active blood clots, severe valve disease, or uncontrolled high BP may not be eligible.
Que: Is EECP covered by insurance in India or globally?
Ans: Coverage varies; in some countries and under some plans, EECP is reimbursed. Check with your provider.
Que: Where can I find EECP treatment centers for angina in India?
Ans: EECP therapy is available at advanced heart clinics, non-invasive cardiology centers, and select hospitals across India.
References:
- Bondesson SM, et al. One year follow-up of patients with refractory angina pectoris treated with enhanced external counterpulsation. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2006.
- Sardari A, et al. Adverse events and their management during enhanced external counterpulsation treatment in patients with refractory angina pectoris. International Journal of Nursing Practice, 2021.
- Rampengan SH, et al. Safety and effectiveness of enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) in refractory angina patients: A systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Annals of Medicine and Surgery, 2022.
- Lawson WE, et al. Two-year clinical outcomes after enhanced external counterpulsation therapy in patients with refractory angina pectoris and left ventricular dysfunction. American Journal of Cardiology, 2005.
- Kumar A, et al. The Effect of Enhanced External Counterpulsation on Quality of life in Patient with Coronary Artery Disease not Amenable to PCI or CABG. Indian Heart Journal, 2020.
- Henry TD, et al. Predictors of treatment benefits after enhanced external counterpulsation in patients with refractory angina pectoris. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 2021.
- Nichols WW, et al. Enhanced external counterpulsation treatment improves arterial wall properties and wave reflection characteristics in patients with refractory angina. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2006.
- Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: projections from 2025 to 2050. European Heart Journal, 2024.

