What is Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin. This condition can range from mild to severe and life-threatening. In this comprehensive blog, we will explore pancreatitis in detail – its types, causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how it can be effectively managed.
Types of Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis primarily comes in two forms:
1. Acute Pancreatitis
- Sudden inflammation that can last from a few days to several weeks
- 80% of cases have mild symptoms and recover completely
- 20% of cases can be severe, leading to complications like organ failure and infections
2. Chronic Pancreatitis
- Long-lasting inflammation that causes permanent damage to the pancreas
- Usually develops gradually over many years
- Can cause permanent loss of pancreatic function, leading to diabetes and digestive problems
Global Statistics
Pancreatitis represents a significant health concern worldwide:
- Globally, the incidence of acute pancreatitis ranges between 13-45 per 100,000 people
- In India, it occurs at a rate of approximately 6-7 cases per 100,000 people, but this is increasing
- Men are more affected than women, especially in chronic pancreatitis
- Higher cases are observed in urban areas
- In India, alcohol consumption and gallstones are the leading causes of pancreatitis
Global Statistics on Pancreatitis
-
Every year, around 3 to 5 million people globally suffer from Acute Pancreatitis.
-
According to WHO, patients with Chronic Pancreatitis often experience 40% or more digestive complications.
-
In India, alcohol, high-fat diet, and gallstones are among the top causes.
Causes of Pancreatitis
Major Causes of Acute Pancreatitis:
- Gallstones – The most common cause in India (40-50% of cases)
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption – The second most common cause (30-35% of cases)
- Medication Side Effects – Certain antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and painkillers
- Hypertriglyceridemia – High levels of triglycerides in the blood
- Hypercalcemia – High levels of calcium in the blood
- Pancreatic Tumors
- Post-procedural – Following procedures like ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
- Genetic Causes
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Infections – Certain viral infections like mumps
Major Causes of Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Long-term Alcohol Abuse – In approximately 70% of cases
- Genetic Causes – Particularly mutations in PRSS1, SPINK1, and CFTR genes
- Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis
- Obstructive Pancreatitis
- Age-related Factors
Symptoms and Signs of Pancreatitis
Symptoms of Acute Pancreatitis:
- Severe Abdominal Pain – In the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Fever
- Yellowing of Skin and Eyes (Jaundice)
- Rapid Heart Rate (Tachycardia)
- Abdominal Swelling and Tenderness
- Difficulty Breathing
Symptoms of Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Persistent Abdominal Pain – Which may worsen after eating
- Vomiting and Nausea
- Weight Loss
- Sever Back Pain
- Unintended Weight Loss
- Fatty Stool (Steatorrhea) – Greasy, foul-smelling stools
- Symptoms of Diabetes – Excessive thirst, frequent urination
- Loss of Appetite
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Digestive Issues and Malabsorption
Lifestyle Challenges for Pancreatitis Patients
Patients with pancreatitis face the following challenges:
- Chronic Pain Management – Managing pain in chronic pancreatitis can be challenging
- Dietary Restrictions – Low-fat diet, small meals, avoiding certain foods
- Alcohol Abstinence – Complete abstinence from alcohol is essential
- Impaired Digestion and Nutrition – Pancreatic enzyme deficiency necessitating enzyme supplements
- Diabetes Management – Chronic pancreatitis often causes diabetes
- Medication Side Effects – From painkillers and other medications
- Frequent Hospitalizations – Due to acute flare-ups
- Mental Health Impact – Depression and anxiety due to chronic pain, dietary restrictions, and reduced quality of life
- Work and Social Life Impact – Work absenteeism and social isolation due to the condition
- Financial Burden – Due to long-term treatment and hospitalizations
Treatment Options for Pancreatitis
Conventional Treatment
For Acute Pancreatitis:
- Hospitalization – Required in most cases
- IV Fluid and Electrolyte Replacement
- Pain Management – Pain-relieving medications
- Food Restriction – To rest the pancreas
- Antibiotics for Infections – If necessary
- Surgical or Endoscopic Intervention – For gallstones or pancreatic necrosis
For Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Pain Management – Pain relievers, sometimes narcotics
- Pancreatic Enzyme Supplements
- Insulin or Oral Hypoglycemic Agents – For diabetes management
- Endoscopic or Surgical Procedures:
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
- Stent Placement
- Pancreatic Drainage Procedures
- Partial or Total Pancreatectomy
Integrated Lifestyle and Natural Treatments
- Dietary Modifications:
- Low-fat diet (<30% of daily calories from fat)
- Small and frequent meals
- Avoiding highly processed foods
- Antioxidant-rich foods (fruits and vegetables)
- Adequate protein and carbohydrates
- Alcohol and Smoking Cessation:
- Complete abstinence from alcohol
- Quitting smoking
- Hydration:
- Drinking adequate water daily (approximately 2-3 liters)
- Ayurvedic Treatments:
- Triphala Churna
- Shatavari
- Ashwagandha
- Giloy
- Yoga and Pranayama:
- Vajrasana
- Pawanmuktasana
- Ardha Matsyendrasana
- Anulom-Vilom Pranayama
- Bhramari Pranayama
- Herbs and Supplements:
- Curcumin (Turmeric)
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Probiotics
- Vitamin D and Calcium
- Stress Management:
- Meditation
- Deep Breathing Exercises
- Mind-Body Techniques
Conventional vs. Integrated Treatment: Comparative Chart
| Aspect | Conventional Treatment | Integrated Lifestyle Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Symptom-focused | Holistic approach |
| Focus | Immediate relief and complication management | Addressing root causes and promoting wellness |
| Effectiveness | Faster relief in acute phase | Better in long-term management |
| Side Effects | More likely (especially from pain medications) | Lower risk |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More economical in the long run |
| Patient Participation | Less required | Highly required |
| Recurrence Prevention | Limited | Better outcomes |
| Quality of Life | May be reduced during treatment | Likely to improve |
What is Pancreatitis – Effective Management
Long-term Management Strategies:
Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Evaluation of pancreatic function
- Monitoring for diabetes
- Assessment of nutritional status
Self-care:
- Symptom monitoring
- Recognising warning signs
- Medication adherence
- Following dietary guidelines
Support Groups:
- Sharing experiences
- Gaining emotional support
- Obtaining practical advice
Integrated Approach:
- Conventional medicine
- Ayurveda
- Lifestyle modifications
- Dietary therapy
Living a Long and Healthy Life with Pancreatitis
Essential steps for living a healthy and meaningful life with pancreatitis:
- Complete Abstinence from Alcohol – This is the most crucial step
- Adopting Healthy Dietary Patterns – Low fat, high fiber
- Quitting Smoking
- Regular Physical Activity – Light to moderate exercise
- Maintaining Adequate Hydration
- Following Medical Instructions – Medications and supplements
- Adopting Stress Management Techniques
- Building a Support Network – Family, friends, and support groups
- Regular Medical Check-ups – Monitoring pancreatic condition
- Positive Mental Attitude – Learning to live with the condition
Conclusion
Pancreatitis is a serious condition that requires proper management. While it can be challenging, with a combination of healthy lifestyle choices, dietary modifications, and appropriate medical care, patients can control their symptoms and lead a healthy life.
If you or your loved one is struggling with pancreatitis, book an appointment with our specialists today. Our integrated approach can help you effectively manage your condition and achieve a better quality of life.
Take the Next Step Toward Healing
Who is Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar?
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is an experienced Clinical Nutritionist and the Founder of Fit My Heart. With over 11 years of experience, he has helped thousands of patients reverse liver, pancreas, heart, and metabolic diseases through non-invasive and drug-free methods. His mission is to provide root-cause healing through lifestyle and nutrition.
📲 Book Your Consultation Now
If you or someone in your family is suffering from Pancreatitis, don’t delay.
👉 Consult us today and take your first step toward a pain-free, healthy life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pancreatitis
Understanding Pancreatitis
1. What is pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas, a gland located behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and insulin. The inflammation occurs when digestive enzymes become activated while still in the pancreas, causing irritation and damage to the organ’s tissues.
2. What is the difference between acute and chronic pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is sudden inflammation that typically resolves within days to weeks with proper treatment. Chronic pancreatitis is persistent inflammation that develops over many years, causing permanent damage to the pancreas and impairing its function.
3. What are the main causes of pancreatitis?
The most common causes of acute pancreatitis are gallstones (40-50% of cases) and excessive alcohol consumption (30-35% of cases). Chronic pancreatitis is primarily caused by long-term alcohol abuse (70% of cases), genetic factors, recurrent acute pancreatitis, and autoimmune conditions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
4. What are the warning signs of pancreatitis?
The primary symptom is severe upper abdominal pain that may radiate to the back. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fever, rapid heart rate, and tender abdomen. Chronic pancreatitis may additionally present with weight loss, oily stools, and symptoms of diabetes.
5. When should I seek emergency medical attention for suspected pancreatitis?
Seek immediate medical care if you experience severe abdominal pain (especially with nausea and vomiting), pain so intense you cannot find a comfortable position, abdominal pain radiating to your back, fever with abdominal pain, or yellowing of the skin or eyes.
6. How is pancreatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure pancreatic enzyme levels (amylase and lipase), imaging studies such as CT scans or ultrasound, and sometimes more specialized tests like endoscopic ultrasound or ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography).
Treatment and Management
7. Can pancreatitis be cured?
Acute pancreatitis can often be resolved with proper treatment. Chronic pancreatitis, however, cannot be cured as the damage is permanent, but symptoms can be managed effectively with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications.
8. What dietary changes are recommended for pancreatitis patients?
Patients should follow a low-fat diet (less than 30% of daily calories from fat), eat smaller and more frequent meals, avoid alcohol completely, limit processed foods, increase consumption of fruits and vegetables, and stay well-hydrated.
9. Why is alcohol abstinence so important for pancreatitis patients?
Alcohol directly damages pancreatic cells and is a major cause of both acute and chronic pancreatitis. Even small amounts can trigger severe pain and inflammation in patients with existing pancreatic damage. Complete abstinence is essential to prevent further damage and recurrent attacks.
10. What medications are used to treat pancreatitis?
Treatments may include pain medications, pancreatic enzyme supplements (for chronic pancreatitis), insulin (if diabetes develops), and sometimes antibiotics (if infection is present). The specific medications depend on the type of pancreatitis and individual symptoms.
Complications and Long-term Outlook
11. What are the potential complications of untreated pancreatitis?
Untreated pancreatitis can lead to serious complications including pancreatic necrosis (tissue death), pseudocysts, infection, kidney failure, breathing problems, diabetes, malnutrition, and in severe cases, multi-organ failure or death.
12. Does pancreatitis increase the risk of pancreatic cancer?
Yes, chronic pancreatitis is associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. The risk is approximately 5% within 20 years of diagnosis and is higher in those with hereditary forms of pancreatitis.
Natural Approaches and Prevention
13. Can yoga and meditation help manage pancreatitis?
Yes, certain yoga postures like Vajrasana, Pawanmuktasana, and Ardha Matsyendrasana may help improve digestion and reduce stress. Breathing exercises (pranayama) and meditation can help manage pain and reduce stress, which may help prevent flare-ups.
14. What supplements may be beneficial for pancreatitis patients?
Some potentially beneficial supplements include curcumin (from turmeric) for its anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 fatty acids to reduce inflammation, probiotics to support gut health, and vitamin D and calcium supplements to prevent osteoporosis, which is common in chronic pancreatitis.
15. How can I prevent pancreatitis recurrence?
Prevention strategies include complete abstinence from alcohol, following a low-fat diet, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, taking prescribed medications as directed, attending regular medical check-ups, and promptly treating any underlying conditions like gallstones or high triglycerides.
EECP Therapy for Heart Failure: A Revolutionary Non-Invasive Treatment Option
Posted byEECP Therapy for Heart Failure: Heart failure affects millions worldwide, causing significant suffering and economic burden. Among the various treatment options available today, Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) therapy for heart failure has emerged as a promising non-invasive approach, particularly for patients with ischemic heart failure. This blog explores the science behind EECP therapy for heart failure, its effectiveness, ideal candidates, and what patients can expect from this treatment.
Understanding Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Despite its name, heart failure doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working—rather, it means the heart isn’t working as efficiently as it should. This serious condition affects approximately 6.2 million adults in the United States alone.
Types of Heart Failure
Heart failure can be categorized based on which side of the heart is affected:
Left-sided heart failure: The most common type, occurs when the left ventricle cannot pump blood effectively
Right-sided heart failure: Often results from left-sided failure, occurs when the right ventricle cannot effectively pump blood to the lungs
Biventricular heart failure: Affects both sides of the heart
Heart failure can also be classified based on ejection fraction (EF)—the percentage of blood pumped out with each contraction:
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): EF less than 40%
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): EF greater than or equal to 50%
Heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction: EF between 40-49%
Causes of Heart Failure
The primary causes of heart failure include:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): According to research, CAD is responsible for approximately 48.3% of heart failure cases in China and remains a leading cause worldwide
- Hypertension
- Valvular heart disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defects
- Arrhythmias
- Diabetes
- Alcohol or drug abuse
Symptoms of Heart Failure
Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath during activity or when lying down
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Persistent cough or wheezing
- Increased need to urinate, especially at night
- Sudden weight gain from fluid retention
Conventional Treatments for Heart Failure
Before diving into EECP therapy for heart failure, let’s review the conventional treatment approaches:
Medications
Standard medications for heart failure include:
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs to widen blood vessels
- Beta-blockers to slow heart rate and reduce blood pressure
- Diuretics to reduce fluid buildup
- Aldosterone antagonists to help the body eliminate salt and water
- SGLT2 inhibitors, which have shown remarkable benefits in recent years
- Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs)
- Digoxin to strengthen heart contractions
- Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
Devices and Surgical Interventions
When medications aren’t enough, doctors may recommend:
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs)
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT)
- Left ventricular assist devices (LVADs)
- Heart valve repair or replacement
- Coronary bypass surgery
- Heart transplantation
Despite these options, many patients continue to experience symptoms or may not be eligible for invasive procedures. This is where EECP therapy for heart failure comes into the picture.
What is EECP Therapy for Heart Failure?
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) is a non-invasive treatment that uses carefully timed compression of the lower extremities to increase blood flow to the heart. The therapy involves wrapping pressure cuffs around the patient’s calves, thighs, and buttocks. These cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the patient’s heartbeat:
- During diastole (when the heart is relaxing): The cuffs inflate sequentially from the calves upward
- During systole (when the heart is contracting): The cuffs rapidly deflate
This sequential compression creates a “counterpulsation” effect that:
- Increases blood flow to the coronary arteries during diastole
- Decreases cardiac afterload during systole
- Enhances venous return to the heart
A standard course of EECP therapy for heart failure typically consists of 35 one-hour sessions, usually administered 5 days a week for 7 weeks.
The Potential Mechanisms by Which EECP Improves Heart Function:
At this stage, the effects of EECP are primarily categorized into immediate hemodynamic changes and long-term anti-ischemic benefits driven by shear stress, though other potential mechanisms remain to be explored.
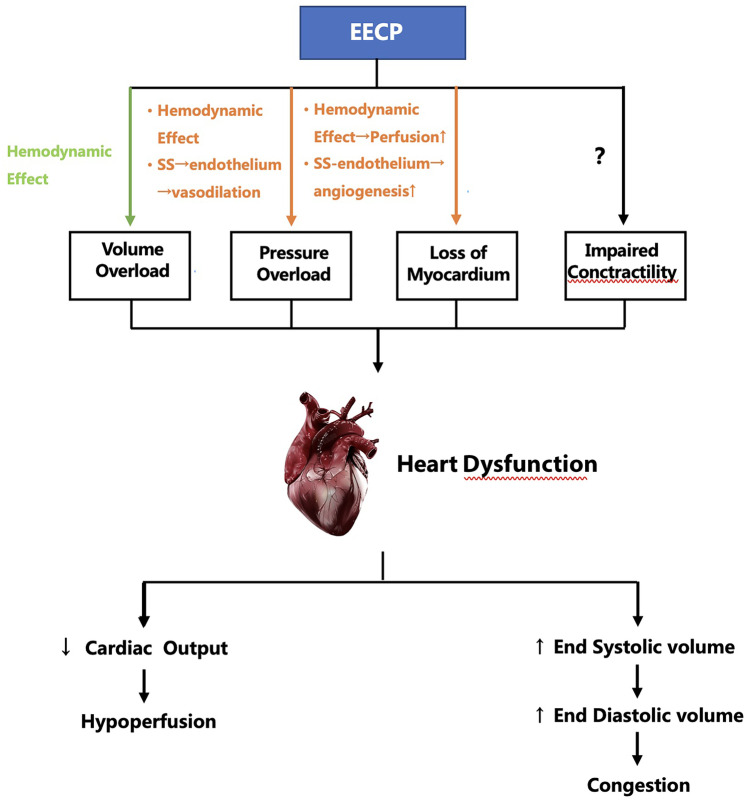
The potential mechanisms by which EECP improves heart failure. EECP, enhanced external counterpulsation; SS, shear stress; green arrow: may be harmful; orange arrow: helpful
EECP Therapy for Heart Failure: The Science of Working
The research paper provides valuable insights into the mechanisms by which EECP therapy improves heart failure:
Immediate Hemodynamic Effects
- Increased coronary perfusion: EECP therapy increases diastolic blood pressure by 26-157%, significantly improving blood flow to the heart muscle
- Reduced cardiac afterload: Synchronous release of all cuffs during systole can reduce systolic blood pressure by 9-16 mmHg
- Decreased left ventricular energy consumption: Studies using pulse wave analysis technology found reduced myocardial oxygen demand after EECP treatment
Long-term Effects Mediated by Shear Stress
EECP therapy for heart failure creates beneficial shear stress on blood vessel walls, which leads to:
Improved endothelial function:
- Increased production of nitric oxide (NO) and other vasodilators
- Decreased production of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and other vasoconstrictors
- Enhanced endothelial cell-dependent vasodilation
Angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels):
- Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
- Increased angiopoietin production
- Enhanced proliferation and differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells
Anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects:
- Regulation of inflammatory factors
- Reduction in oxidative stress
- Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques
Potential direct effects on cardiac contractility:
- Increased plasma adrenomedullin (ADM) levels
- Possible improvements in mitochondrial function
- Potential effects on calcium ion currents in ventricular myocytes
These mechanisms collectively contribute to improved myocardial perfusion, reduced cardiac workload, and enhanced heart function.
Clinical Evidence for EECP Therapy in Heart Failure
Multiple studies have demonstrated the benefits of EECP therapy for heart failure patients:
The PEECH Study
This randomized controlled trial included 130 patients with ischemic heart failure (NYHA class II-III) and found:
- Significant improvements in NYHA classification
- Enhanced quality of life
- Increased total exercise time
- Higher peak oxygen uptake (VO₂peak) one week after treatment
Effects on Performance Status
Studies consistently show that EECP therapy for heart failure improves:
- Exercise capacity (total exercise time)
- 6-minute walk test performance
- NYHA functional classification
Effects on Cardiac Function
Systolic Function
Results on left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are mixed:
- Some studies show no significant improvement
- Others demonstrate marked improvement, especially in patients with baseline LVEF <40%
- Global longitudinal strain (GLS) measurements show promising improvements
Diastolic Function
Studies consistently show improvements in diastolic function markers:
- Enhanced E/A ratio (0.92 ± 0.41 vs. 1.08 ± 0.46, P<0.05)
- Improved E/Ea ratio (12.61 ± 4.22 vs. 15.44 ± 6.96, P<0.05)
- Better peak filling rate (PFR)
The E/A ratio is a measurement used to assess cardiac diastolic function (how well the heart fills with blood between contractions), which I mentioned in the “Effects on Cardiac Function” section of the blog post.
The E/A ratio is an echocardiographic measurement derived from Doppler imaging that evaluates how blood flows through the mitral valve between the left atrium and left ventricle during diastole (the filling phase of the cardiac cycle). It consists of two components:
- E wave (Early diastolic filling): Represents passive filling of the ventricle when the mitral valve first opens. This is the first and usually larger peak on the Doppler waveform.
- A wave (Atrial contraction): Represents the additional blood flow into the ventricle caused by atrial contraction (the “atrial kick”). This is the second peak on the Doppler waveform.
The E/A ratio is calculated by dividing the peak E wave velocity by the peak A wave velocity.
From the Research it has been found that, patients who received EECP therapy showed an improvement in their E/A ratio from 0.92 ± 0.41 to 1.08 ± 0.46 (P < 0.05), indicating enhanced diastolic function after treatment.
A normal E/A ratio typically ranges from about 0.8 to 2.0, depending on age. In heart failure with diastolic dysfunction, this ratio is often abnormal:
- In early/mild diastolic dysfunction: The ratio may be reduced (<0.8)
- In moderate diastolic dysfunction: The ratio may appear pseudonormal (normal-looking but with other abnormal parameters)
- In severe diastolic dysfunction: The ratio may be elevated (>2.0), known as a “restrictive filling pattern”
The improvement in E/A ratio after EECP therapy suggests that this treatment helps the heart fill more efficiently during diastole, which is particularly important for heart failure patients.
Effects on Prognosis
EECP therapy for heart failure appears to improve short-term outcomes:
- Reduced 90-day readmission rates (6.1% vs. predicted 34%)
- 78% reduction in emergency room visits over 6 months
- 73% reduction in hospitalizations over 6 months
Ideal Candidates for EECP Therapy for Heart Failure
Based on clinical studies and guidelines, the following patients may benefit most from EECP therapy:
Recommended Candidates:
- Patients with stable ischemic heart failure (NYHA class II-III)
- Individuals with angina symptoms combined with heart failure
- Heart failure patients with coronary artery disease as the primary cause
- Patients who have exhausted standard medical therapies
- Individuals who are not candidates for invasive procedures
- Elderly patients (studies show particularly good results in those over 65)
- Patients seeking to improve exercise tolerance and quality of life
Comparing EECP Therapy with Surgical Options and ICDs
When considering treatments to improve heart function, patients and clinicians have several options. Here’s how EECP therapy for heart failure compares to surgical interventions and implantable devices:
| Aspect | EECP Therapy for Heart Failure | Heart Surgery (CABG/Valve) | ICD/CRT Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive, external | Highly invasive | Minimally invasive |
| Anesthesia | None required | General anesthesia | Local anesthesia |
| Hospital stay | Outpatient procedure | 5-7 days | 1-2 days |
| Recovery time | None, resume normal activities | 6-12 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Treatment duration | 35 one-hour sessions over 7 weeks | One-time procedure | One-time implantation |
| Mechanism | Increases coronary perfusion, reduces afterload | Direct revascularization or valve repair | Corrects rhythm or synchronizes contractions |
| Effect on survival | Limited data on long-term survival | Improved survival in selected patients | Improved survival in appropriate candidates |
| Effect on symptoms | Significant symptom improvement | Variable symptom improvement | Variable symptom improvement |
| Exercise capacity | Consistently improved | Variable improvement | Variable improvement |
| Risk of serious complications | Very low | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Retreatment possibility | Can be repeated as needed | Redo surgery is high risk | Battery replacement needed every 5-10 years |
| Cost | Moderate | Very high | High |
| Insurance coverage | Variable | Generally covered | Generally covered |
Contraindications: Who Should Not Receive EECP Therapy for Heart Failure
Although EECP therapy for heart failure is generally safe, it’s not appropriate for everyone. Contraindications include:
Absolute Contraindications:
- Acute heart failure decompensation
- Severe aortic insufficiency (regurgitation)
- Acute deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Severe peripheral arterial disease with ulcers
- Pregnancy
- Arrhythmias that interfere with ECG triggering
- Coagulopathy with active bleeding
Relative Contraindications:
- Hypertension uncontrolled by medication (>180/110 mmHg)
- Recent cardiac catheterization or arterial puncture (<2 weeks)
- Severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm >4 cm
- Moderate to severe aortic stenosis
- Recent stroke (<3 months)
- Heart rate >120 beats per minute
What to Expect During EECP Therapy for Heart Failure
For patients considering EECP therapy, here’s a guide to the treatment experience:
Before Treatment:
- Comprehensive evaluation: Medical history review, physical examination, and possibly cardiac tests
- Treatment planning: Discussion of the number of sessions needed (typically 35)
- Insurance verification: Checking coverage for the procedure
During Treatment:
Preparation:
- The patient lies on a comfortable treatment table
- ECG electrodes are attached to monitor heart rhythm
- Blood pressure cuff is placed on one arm
- Pressure cuffs are wrapped around calves, thighs, and buttocks
The procedure:
- Each session lasts approximately one hour
- The cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the heartbeat
- Patients may feel pressure similar to a tight hug on their legs
- Most patients find the treatment comfortable enough to read, watch TV, or even nap
Monitoring:
- Heart rhythm and blood pressure are continuously monitored
- Healthcare providers check for any discomfort or side effects
After Treatment:
Immediate effects:
- Most patients can resume normal activities immediately
- Some may experience mild fatigue or muscle soreness
Follow-up care:
- Regular assessments throughout the course of therapy
- Evaluation of symptoms and functional capacity
- Adjustment of medications as needed
Potential side effects:
- Minor discomfort like skin irritation or bruising
- Muscle or joint soreness
- Rarely, dizziness or fatigue
Expected Outcomes:
Based on clinical studies, patients may experience:
- Noticeable improvement in symptoms after 15-20 sessions
- Reduced shortness of breath
- Increased exercise tolerance
- Better quality of life
- Decreased need for nitrate medications (if used for angina)
- Reduction in emergency room visits and hospitalizations
The Future of EECP Therapy for Heart Failure
As research continues, several exciting developments are on the horizon:
- Personalized treatment protocols: Tailoring the number and frequency of sessions to individual patient needs
- Combination therapies: Integrating EECP with other treatments for synergistic effects
- Improved devices: More comfortable, efficient, and portable EECP machines
- Expanded indications: Potential use in other cardiovascular conditions
- Long-term efficacy data: More research on the durability of benefits
Conclusion
EECP therapy for heart failure represents a valuable non-invasive option for patients with ischemic heart failure, particularly those who have exhausted conventional treatments or are not candidates for invasive procedures. The therapy’s ability to improve myocardial perfusion, reduce cardiac workload, and enhance both systolic and diastolic function makes it a promising addition to the heart failure treatment arsenal.
Clinical evidence demonstrates that EECP therapy for heart failure can significantly improve functional capacity, quality of life, and short-term outcomes like hospitalizations. While more research is needed—especially regarding long-term benefits and direct effects on cardiac contractility—the existing data supports EECP therapy for heart failure as a safe and effective treatment option.
For heart failure patients seeking symptom relief and improved quality of life, EECP therapy for heart failure deserves consideration as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. As with any medical treatment, patients should consult with their cardiologists to determine if EECP therapy for heart failure is appropriate for their specific condition.
Meet Vivek Singh Sengar – EECP Expert & Founder of Fit My Heart
Vivek Singh Sengar is a renowned Clinical Nutritionist and EECP Therapy Specialist, with over 11 years of experience in reversing heart failure and coronary blockages through non-invasive, drug-free treatments. As the Founder of Fit My Heart, he has helped thousands of patients avoid bypass surgery and improve their heart function using personalized EECP therapy and lifestyle protocols.
✅ Struggling with Heart Failure?
You Deserve a Second Opinion – Without Surgery or Stents
🔹 Book a FREE 15-minute consultation with Vivek Singh Sengar
🔹 Understand if EECP Therapy is right for your heart condition
🔹 Get a personalized, non-surgical treatment plan
👉 Book Your Free Consultation Now
Take the first step toward a stronger heart – naturally.
Frequently Asked Questions About EECP Therapy for Heart Failure
Que: What exactly is EECP therapy for heart failure?
Ans: EECP is a non-invasive treatment that uses inflatable cuffs on the legs to increase blood flow to the heart and improve cardiac function by synchronizing compression with the patient’s heartbeat.
Que: How long does a complete course of EECP therapy take?
Ans: A standard course consists of 35 one-hour sessions, typically administered 5 days a week for 7 weeks.
Que: Is EECP therapy painful?
Ans: No, it’s not painful. Most patients describe a sensation of pressure similar to a tight hug on their legs, and many find it comfortable enough to read or nap during treatment.
Que: How soon might I notice improvements with EECP therapy for heart failure?
Ans: Many patients report noticeable symptom improvement after 15-20 sessions, though individual responses vary.
Que: Is EECP therapy covered by insurance?
Ans: In USA Coverage varies by provider. EECP is covered by Medicare and many insurance plans for specific indications, but verification is recommended before starting treatment. In INDIA, insurance companies usually do not cover EECP Treatment, but It purely depends upon the patient and doctor. Usually, a patient is required to talk to his doctor and insurance company. It has been seen that many patients get the reimbursement after submitting all the valid documents and consistent follow-up with the insurance company and the doctor.
Que: Can EECP therapy replace medications for heart failure?
Ans: No, EECP is typically used as a complementary treatment alongside standard medications, not as a replacement but in most of the cases the need for medicines is reduced post EECP therapy.
Que: Are the effects of EECP therapy permanent?
Ans: Benefits typically last 3-5 years, after which some patients may require repeat courses of therapy or booster doze can be taken to maintain the effect of EECP Therapy.
Que: Can I have EECP therapy if I have an ICD or pacemaker?
Ans: Yes, having a pacemaker or ICD is not a contraindication for EECP therapy.
Que: What side effects might occur with EECP therapy?
Ans: Common side effects are mild and include skin irritation, muscle soreness, or fatigue. Serious side effects are rare.
Que: How does EECP therapy differ from cardiac rehabilitation?
Ans: While cardiac rehab focuses on exercise and lifestyle changes, EECP is a passive treatment that mechanically improves blood flow without requiring physical exertion.
Que: Can EECP therapy help if I’m waiting for a heart transplant?
Ans: Yes, EECP may be used as a “bridge therapy” to improve quality of life and function while waiting for transplantation, in most cases EECP Therapy may avoid the need for the Heart Transplantation.
Que: Is there an age limit for EECP therapy?
Ans: There’s no specific age limit, and studies show elderly patients (over 65) often respond particularly well to treatment.
Que: Can EECP therapy reduce my need for heart medications?
Ans: Most of the patients require fewer medications after EECP therapy, but any changes should only be made under physician supervision.
Que: How is success of EECP therapy measured?
Ans: Success is measured through improved symptoms, exercise capacity, quality of life, echocardiographic parameters, and reduced hospitalizations.
Que: Can I resume normal activities while undergoing EECP therapy?
Ans: Yes, most patients can maintain their normal daily activities during the treatment period with no restrictions.
Enhanced External Counterpulsation: 3 Unique Benefits of EECP
Posted byEnhanced External Counterpulsation: What is EECP?
-
EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) is a non-invasive circulatory support technique.
-
It uses inflatable cuffs (like blood pressure cuffs) placed on the legs and buttocks.
-
The cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the heartbeat, improving blood flow to the heart, brain, and other vital organs.
-
It enhances circulation by increasing venous return and diastolic aortic pressure, which improves myocardial function.
How Does Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) Work?
-
Sequential inflation of the cuffs squeezes blood from the legs toward the heart.
-
The inflation occurs during the heart’s resting phase (diastole) to boost blood supply.
-
It helps open smaller blood vessels, reduces inflammation, and supports vessel repair.
-
Benefits include:
-
Increased blood flow to vital organs (heart, brain, kidneys)
-
Improved heart function and reduced stress
-
Support for brain recovery after stroke
-
Better blood sugar control in diabetics
-
Who Can Benefit from Enhanced External Counterpulsation EECP?
EECP is especially helpful for patients with the following conditions:
-
Cardiovascular Issues:
-
Angina (chest pain)
-
Heart failure
-
Past heart attacks
-
-
Neurological Disorders:
-
Ischemic stroke
-
Parkinson’s disease
-
Alzheimer’s disease
-
-
Metabolic and Other Conditions:
-
Type 2 diabetes (and its complications)
-
Eye diseases due to poor blood flow
-
Sleep disorders
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Sudden hearing loss
-
Depression or anxiety due to chronic illness
-
Also Read: EECP Treatment for Old Age Patients
Who Should Not Receive EECP? (Contraindications)
-
Blood clots in the legs
-
Severe heart valve problems (e.g., severe aortic regurgitation)
-
Uncontrolled high blood pressure
-
Irregular heartbeat not well-managed
-
Open wounds or skin infections on the legs
-
High lung pressure
How is EECP Administered?
-
Standard Protocol:
-
1 hour/day, 5–6 days/week for 6–7 weeks (total of 35–36 hours)
-
-
Cuffs are placed on:
-
Calves
-
Thighs
-
Buttocks
-
-
Monitoring includes:
-
Blood pressure
-
Heart rate and rhythm
-
Oxygen saturation
-
Skin condition
-
-
Adjustments:
-
Based on patient comfort and response
-
Treatment stopped if oxygen drops or pain occurs
-
How to Prepare for EECP
-
Keep stomach empty for at least 2–3 hours before the session
-
Empty your bladder for comfort before starting
-
Take prescribed medications as advised by your doctor
-
Wear loose, comfortable clothing; avoid tight undergarments
-
Avoid caffeine or heavy meals right before treatment
-
Stay relaxed and calm; deep breathing may help
-
Avoid using mobile phones or talking during the session
-
Inform staff if you feel discomfort, pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath
-
Remove jewelry or objects around waist and thighs
-
Bring water and a light snack for after the session if needed
Safety and Monitoring
-
Patients should be screened before starting EECP.
-
Ongoing monitoring during sessions is essential.
-
Doctors adjust cuff pressure and timing as needed.
-
EECP is generally safe and well-tolerated with proper care.
Treatment Maintenance and Follow-up
-
Shorter sessions can be used for less fit or frail patients.
-
Booster treatments can be repeated yearly.
-
Maintenance therapy may include 2–3 hours/week after initial cycle.
Benefits of EECP
-
Reduces chest pain and improves exercise tolerance
-
Enhances heart and brain function
-
Supports recovery after heart procedures or stroke
-
Improves quality of life in elderly patients
-
Helps manage:
-
Sleep and mood disorders
-
Blood sugar in diabetics
-
Vision and hearing loss
-
Sexual dysfunction
-
Conclusion
EECP is a safe, non-invasive, and effective treatment option for elderly individuals with cardiovascular, neurological, and metabolic conditions. It is especially valuable for those who are not good candidates for surgery or strong medications. With proper screening, individualized protocols, and professional monitoring, EECP significantly improves symptoms, functionality, and overall quality of life.
About Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a highly respected EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) expert with over 13 years of clinical experience in the field of non-invasive cardiology and integrative care. As the Founder of FIT MY HEART, he has dedicated his career to providing advanced EECP therapy to patients suffering from chronic heart conditions such as heart failure, angina, low ejection fraction, post-heart attack recovery, and coronary blockages.
Trained in Clinical Nutrition and Integrative Cardiac Rehabilitation, Mr. Sengar blends modern science with lifestyle medicine to deliver holistic, drug-free heart care. He has treated thousands of patients who were either ineligible for bypass or angioplasty, helping them regain functional capacity, improve heart pumping, and reverse symptoms—often without surgery.
His approach combines EECP with chrono-nutrition, therapeutic fasting, herbal support, Panchakarma, and patient education to address root causes rather than just symptoms. Mr. Sengar is also the creator of India’s first 60-hour EECP training program for healthcare professionals and is widely regarded as a pioneer in the expansion of EECP in India for both cardiac and non-cardiac applications.
With a deep passion for preventive healthcare, Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar continues to inspire trust, transformation, and long-term wellness in patients across the country.
