Natural Heart Blockage Treatment without Surgery: Heart disease remains a silent epidemic threatening millions worldwide. While conventional medicine often prescribes surgical interventions for coronary artery blockages, revolutionary non-surgical approaches are proving their effectiveness in reversing heart disease naturally. This comprehensive guide explores evidence-based alternatives that can help restore cardiovascular health without the risks and complications associated with invasive procedures.The journey toward optimal heart health doesn’t always require a scalpel. Modern medical research has unveiled powerful non-invasive therapies that address arterial blockages at their root cause, promoting natural healing and regeneration of cardiovascular tissue.
Global Statistics: The Cardiovascular Crisis
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year. This staggering statistic represents more than just numbers – it reflects the urgent need for effective, accessible treatment options that don’t rely solely on surgical interventions.
In the United States, someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds. Every year, about 805,000 people in the United States have a heart attack. These alarming figures highlight the critical importance of preventive and therapeutic approaches that can reverse arterial damage before it progresses to life-threatening stages.
The long-term impact of heart blockage extends far beyond immediate health concerns. Patients with coronary artery disease face reduced quality of life, increased healthcare costs, and significant limitations in daily activities. Traditional surgical approaches, while sometimes necessary, carry inherent risks including infection, bleeding complications, and the potential for repeat procedures.
Furthermore, the economic burden of cardiovascular disease continues to escalate globally. Healthcare systems worldwide struggle to accommodate the increasing demand for cardiac procedures, making non-surgical alternatives not just medically beneficial but economically essential for sustainable healthcare delivery.
Understanding Heart Blockage: Clinical Pathways and Pathogenesis
Heart blockage, medically termed coronary artery stenosis, represents a complex pathophysiological process involving multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms. The pathogenesis begins with endothelial dysfunction, where the inner lining of coronary arteries becomes compromised due to various risk factors including hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and chronic inflammation.
The progression follows a predictable clinical pathway. Initially, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol infiltrates the arterial wall, triggering an inflammatory cascade. Macrophages attempt to clear these lipid deposits but become foam cells, contributing to plaque formation. Over time, these atherosclerotic plaques accumulate calcium deposits, creating rigid arterial narrowing that restricts blood flow to the myocardium.
The disease progression involves several critical stages. Early atherosclerosis begins with fatty streak formation in the arterial intima. These streaks gradually develop into fibrous plaques containing smooth muscle cells, connective tissue, and lipid cores. Advanced lesions may become unstable, prone to rupture, and capable of triggering acute coronary events.
Understanding this pathophysiology is crucial for developing effective non-surgical interventions. Natural heart blockage treatment approaches target multiple points in this disease progression, addressing inflammation, improving endothelial function, and promoting collateral circulation development.
EECP Treatment: Revolutionary External Counterpulsation Therapy
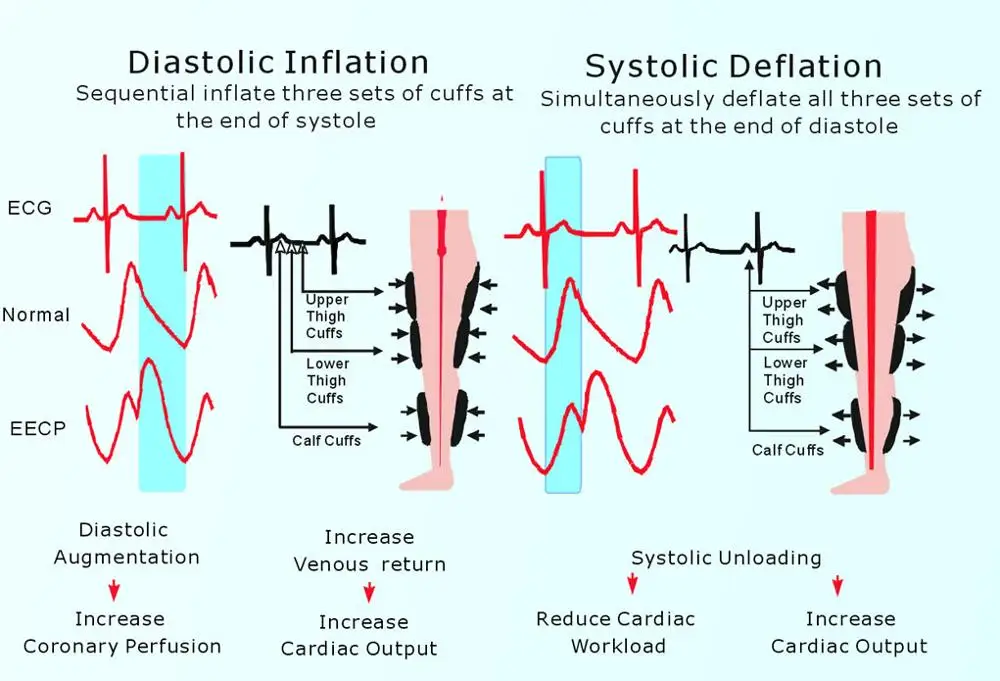
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) represents a groundbreaking advancement in non-invasive cardiac therapy. This FDA-approved treatment utilizes pneumatic cuffs wrapped around the patient’s legs to provide synchronized compression during the heart’s resting phase, effectively creating a natural bypass mechanism.
During EECP sessions, patients lie comfortably while specialized cuffs inflate and deflate in precise synchronization with their heartbeat. This action increases diastolic pressure, enhancing coronary perfusion and promoting the development of collateral blood vessels. The therapy essentially trains the cardiovascular system to create its own natural bypass routes around blocked arteries.
Clinical studies demonstrate remarkable success rates with EECP therapy. Patients typically experience significant improvement in exercise tolerance, reduction in anginal symptoms, and enhanced overall quality of life. The treatment protocol usually consists of 35 – 40 one-hour sessions administered over seven weeks, making it a comprehensive yet manageable therapeutic option.
The mechanism of action involves multiple beneficial effects. EECP increases venous return to the heart, improves coronary perfusion pressure, and stimulates the release of endothelial growth factors that promote new blood vessel formation. This natural angiogenesis process creates alternative pathways for blood flow, effectively bypassing blocked arteries.
EECP therapy benefits extend beyond immediate symptom relief. Long-term studies show sustained improvement in cardiac function, reduced need for medications, and decreased frequency of hospital admissions. The treatment’s safety profile is excellent, with minimal side effects and contraindications limited to specific cardiac conditions.
Dr. Dean Ornish Research: Lifestyle Medicine Revolution
Dr. Dean Ornish’s program remains the only program scientifically proven in randomized controlled trials to reverse the progression of even severe coronary heart disease by lifestyle changes, without drugs or surgery. This groundbreaking research has fundamentally changed how we approach cardiovascular disease treatment.
More regression of coronary atherosclerosis occurred after 5 years than after 1 year in the experimental group. In contrast, in the control group, coronary atherosclerosis continued to progress and more than twice as many cardiac events occurred. These findings demonstrate the progressive nature of lifestyle-based healing and its superiority over conventional approaches in preventing cardiac events.
The Ornish Program encompasses four primary components: nutrition, exercise, stress management, and social support. The dietary approach emphasizes whole, plant-based foods while eliminating processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive dietary fats. This nutritional framework provides optimal fuel for cardiovascular healing while reducing inflammatory markers.
Exercise protocols in the Ornish approach focus on moderate aerobic activity combined with strength training and flexibility exercises. The program recognizes that excessive high-intensity exercise can actually increase oxidative stress, while moderate, consistent activity promotes optimal cardiovascular adaptation.
Stress management techniques include meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises. Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, promotes inflammation, and accelerates atherosclerotic progression. The program’s stress reduction component directly addresses these pathophysiological mechanisms.
Social support elements recognize the profound impact of relationships on cardiovascular health. Group sessions, family involvement, and community support systems create an environment conducive to long-term lifestyle maintenance and emotional well-being.
Natural Heart Blockage Treatment: Comprehensive Lifestyle Approaches
Natural treatment of heart blockage involves addressing multiple risk factors simultaneously through evidence-based lifestyle interventions. This holistic approach recognizes that cardiovascular disease results from complex interactions between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
Dietary modifications form the cornerstone of natural treatment. Anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and phytonutrients help reduce arterial inflammation and promote endothelial healing. Mediterranean diet patterns have shown particular efficacy in reducing cardiovascular events and supporting arterial health.
Physical activity protocols must be individualized based on current fitness levels and cardiac status. Progressive exercise programs begin with low-intensity activities and gradually increase in duration and intensity. Regular physical activity promotes collateral circulation, improves endothelial function, and enhances overall cardiovascular efficiency.
Sleep optimization plays a crucial role in cardiovascular healing. Quality sleep allows for tissue repair, hormone regulation, and stress recovery. Sleep disorders, particularly sleep apnea, significantly increase cardiovascular risk and must be addressed as part of comprehensive treatment.
Weight management strategies focus on sustainable approaches rather than rapid weight loss. Excess adipose tissue produces inflammatory cytokines that accelerate atherosclerotic progression. Gradual, sustainable weight reduction through dietary modifications and increased physical activity provides optimal cardiovascular benefits.
Ayurvedic Treatments for Heart Health
Ayurvedic medicine offers time-tested approaches for cardiovascular health that complement modern therapeutic strategies. These ancient healing practices focus on balancing the body’s fundamental energies (doshas) and promoting natural healing processes.
Snehan (Oleation Therapy) involves the therapeutic application of medicated oils to nourish tissues and improve circulation. Specific herbal oils containing arjuna, brahmi, and ashwagandha penetrate deep into tissues, promoting cellular regeneration and reducing inflammation. This therapy enhances nutrient delivery to cardiac tissues while supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Swedan (Sudation Therapy) utilizes controlled heat application to promote circulation and eliminate toxins. Steam therapy with cardiac-specific herbs helps dilate blood vessels, improve coronary circulation, and support the body’s natural healing mechanisms. The therapy must be carefully monitored and adapted to individual cardiac status.
Hriday Basti represents a specialized Ayurvedic therapy specifically designed for heart conditions. This treatment involves creating a reservoir of warm medicated oil over the heart region, allowing therapeutic compounds to penetrate deeply into cardiac tissues. The therapy promotes circulation, reduces inflammation, and strengthens cardiac muscle function.
Additional Ayurvedic interventions include specific yoga asanas designed to improve cardiovascular function, pranayama (breathing exercises) that enhance oxygen delivery and reduce stress, and meditation practices that promote parasympathetic nervous system activation.
Herbal formulations in Ayurveda utilize combinations of cardioprotective plants including Terminalia arjuna, Withania somnifera, and Commiphora mukul. These herbs provide antioxidant protection, support healthy cholesterol levels, and promote optimal cardiac function through multiple mechanisms.
Read More:
EECP Treatment in Noida
Detox Drinks and Nutritional Interventions
Strategic nutritional interventions play a vital role in supporting cardiovascular health and promoting arterial healing. Specific detox drinks and nutritional protocols help eliminate toxins, reduce inflammation, and provide essential nutrients for cardiovascular repair.
Green Tea and Matcha Protocols provide powerful antioxidants including epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) that protect against oxidative damage and support healthy cholesterol levels. Regular consumption of high-quality green tea helps reduce LDL oxidation and supports endothelial function.
Pomegranate and Berry Combinations deliver anthocyanins and ellagic acid that promote nitric oxide production and improve arterial flexibility. These compounds help reduce blood pressure and support healthy circulation throughout the cardiovascular system.
Turmeric and Ginger Elixirs provide potent anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce arterial inflammation and support healing processes. Curcumin in turmeric has been shown to improve endothelial function and reduce inflammatory markers associated with cardiovascular disease.
Garlic and Onion Preparations contain organosulfur compounds that support healthy blood pressure levels and promote circulation. Regular consumption helps reduce platelet aggregation and supports optimal cardiovascular function.
Omega-3 Rich Smoothies incorporating flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide essential fatty acids that reduce inflammation and support cardiac cell membrane integrity. These nutrients are crucial for optimal cardiovascular function and healing.
Timing and preparation methods significantly impact the therapeutic efficacy of these nutritional interventions. Morning consumption on an empty stomach often provides optimal absorption, while combining specific nutrients can enhance bioavailability and therapeutic effects.
Fasting Protocols for Cardiovascular Health
Therapeutic fasting protocols offer powerful tools for cardiovascular healing when properly implemented under appropriate supervision. Different fasting approaches provide distinct benefits for heart health and arterial function.
Intermittent Fasting (IF) protocols help optimize metabolic function and reduce cardiovascular risk factors. The 16:8 method involves eating within an 8-hour window and fasting for 16 hours. This approach helps improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote cellular autophagy – the body’s natural cellular cleaning process.
Extended Water Fasting under medical supervision can provide profound cardiovascular benefits. Controlled fasting periods allow the body to redirect energy from digestion toward healing and repair processes. Blood pressure often normalizes, inflammatory markers decrease, and insulin sensitivity improves significantly.
Modified Fasting Approaches such as the Fasting Mimicking Diet provide benefits of traditional fasting while maintaining nutrient intake. These protocols typically involve 5-day cycles of reduced caloric intake with specific nutrient profiles designed to promote cellular regeneration.
Fasting protocols must be carefully individualized based on current health status, medications, and cardiovascular condition. Patients with diabetes, advanced heart disease, or those taking specific medications require modified approaches and close medical supervision.
The physiological benefits of therapeutic fasting include improved lipid profiles, reduced blood pressure, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and activation of cellular repair mechanisms. These effects directly support cardiovascular healing and arterial health improvement.
Homeopathy and Naturopathy Approaches
Homeopathic medicine offers individualized treatment approaches that support the body’s natural healing capacity. Constitutional homeopathic remedies are selected based on the patient’s overall symptom picture, including physical, mental, and emotional characteristics.
Crataegus (Hawthorn) serves as a primary homeopathic remedy for heart conditions. This remedy supports cardiac muscle function, improves circulation, and helps regulate heart rhythm. Different potencies are used based on individual symptom presentations and constitutional factors.
Digitalis in homeopathic preparation helps address specific cardiac symptoms including irregular heartbeat and circulation difficulties. The remedy is particularly beneficial for patients experiencing heart palpitations and associated anxiety.
Cactus Grandiflorus addresses constrictive heart sensations and helps improve coronary circulation. This remedy is often indicated for patients experiencing chest tightness and restricted feeling around the heart.
Naturopathic approaches focus on identifying and addressing root causes of cardiovascular disease while supporting the body’s inherent healing mechanisms. Treatment protocols incorporate multiple therapeutic modalities tailored to individual needs.
Calf Massage and Circulatory Therapies improve venous return and promote overall circulation. Specific massage techniques help stimulate lymphatic drainage and support cardiovascular function through mechanical and reflexive mechanisms.
Hydrotherapy Protocols utilize water temperature variations to promote circulation and support cardiovascular function. Contrast showers, foot baths, and other hydrotherapy applications help strengthen the cardiovascular system and improve adaptive capacity.
Nutritional Medicine in naturopathy emphasizes whole foods, targeted supplementation, and elimination of dietary factors that contribute to cardiovascular disease. Comprehensive nutritional assessments guide individualized therapeutic protocols.
Herbal Medicine for Heart Health
Traditional herbal medicine offers numerous therapeutic options for supporting cardiovascular health and promoting arterial healing. Specific herbs provide targeted benefits through various mechanisms of action.
Terminalia Arjuna stands as one of the most researched cardioprotective herbs. This Ayurvedic medicine contains powerful compounds that strengthen cardiac muscle, improve coronary circulation, and help regulate cholesterol levels. Clinical studies demonstrate significant improvements in exercise tolerance and reduction in anginal symptoms.
Hawthorn (Crataegus species) provides comprehensive cardiovascular support through multiple mechanisms. The herb contains flavonoids and oligomeric procyanidins that improve coronary circulation, strengthen heart muscle contractions, and help regulate heart rhythm. Regular use supports both acute symptoms and long-term cardiovascular health.
Motherwort (Leonurus cardiaca) offers specific benefits for heart rhythm irregularities and stress-related cardiac symptoms. The herb contains compounds that help calm nervous system activity while supporting healthy heart function.
Cayenne Pepper (Capsicum annuum) improves circulation and supports healthy blood pressure levels. The active compound capsaicin helps dilate blood vessels and improve peripheral circulation while providing cardiovascular protective effects.
Ginkgo Biloba enhances circulation and provides antioxidant protection for cardiovascular tissues. The herb helps improve blood flow to coronary arteries and supports overall vascular health through multiple mechanisms.
Herbal protocols must be carefully designed to avoid interactions with medications and to provide optimal therapeutic benefits. Professional guidance ensures safe and effective use of herbal medicines as part of comprehensive cardiovascular treatment.
Treatment Comparison: Non-Surgical vs. Conventional Approaches
| Aspect | Non-Surgical Treatment | Conventional Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive, external therapies | Invasive procedures requiring incisions |
| Recovery Time | Minimal downtime, immediate daily activities | Extended recovery period (6-12 weeks) |
| Risk Profile | Minimal side effects, natural healing | Surgical risks, infection, bleeding complications |
| Long-term Outcomes | Addresses root causes, sustainable improvement | May require repeat procedures, doesn’t address underlying causes |
| Cost Effectiveness | Lower overall costs, reduced hospitalizations | High initial costs, potential complications |
| Treatment Duration | Gradual improvement over 6-12 months | Immediate but temporary symptom relief |
| Lifestyle Integration | Promotes healthy lifestyle changes | Often requires lifestyle changes post-surgery |
| Success Rate | 70-85% improvement in symptoms | 90-95% immediate procedural success |
| Holistic Benefits | Improves overall health and vitality | Focuses specifically on arterial blockage |
| Sustainability | Long-lasting results with lifestyle maintenance | May require additional interventions |
Who Needs Non-Surgical Heart Blockage Treatment?
Non-surgical approaches benefit a wide range of individuals with varying degrees of cardiovascular risk and disease severity. Understanding appropriate candidacy helps optimize treatment selection and outcomes.
Early-Stage Cardiovascular Disease patients with mild to moderate arterial blockages often achieve excellent results with non-surgical approaches. These individuals typically have preserved heart function and the greatest potential for arterial healing and regeneration.
High Surgical Risk Patients who may not be suitable candidates for invasive procedures due to age, comorbidities, or poor surgical risk profiles often find non-surgical treatments provide significant benefits without associated risks.
Patients Seeking Natural Alternatives who prefer to avoid surgical interventions and pharmaceutical dependencies often achieve remarkable results with comprehensive natural treatment protocols.
Prevention-Focused Individuals with family history of heart disease or multiple risk factors can use non-surgical approaches to prevent disease progression and optimize cardiovascular health.
Post-Surgical Patients who have undergone previous cardiac procedures may benefit from non-surgical treatments to prevent restenosis and optimize long-term outcomes.
Individuals with Multiple Comorbidities including diabetes, kidney disease, or other chronic conditions often respond well to holistic approaches that address multiple health concerns simultaneously.
Comprehensive evaluation helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual. Factors including disease severity, symptoms, lifestyle factors, and personal preferences all influence treatment selection and protocol design.
Clinical Outcomes and Evidence-Based Results
Research consistently demonstrates the effectiveness of non-surgical approaches for cardiovascular disease treatment. Multiple clinical studies provide compelling evidence for these therapeutic interventions.
EECP therapy shows remarkable clinical outcomes across diverse patient populations. Studies indicate 70-85% of patients experience significant symptom improvement, with many achieving complete freedom from anginal symptoms. Exercise tolerance typically improves by 30-50%, and quality of life measures show substantial enhancement.
Dean Ornish published results of a randomized clinical trial that used advanced imagery scans to show coronary artery disease could be reversed with nothing more than diet, exercise, stress reduction and social support. This landmark research established the scientific foundation for lifestyle-based cardiac treatment.
Long-term follow-up studies demonstrate sustained benefits from non-surgical treatments. Five-year outcomes show continued improvement in arterial health, reduced cardiac events, and enhanced overall cardiovascular function. These results often surpass conventional surgical approaches in terms of long-term success and patient satisfaction.
Combination treatment protocols incorporating multiple non-surgical modalities show synergistic effects. Patients receiving comprehensive treatment including EECP, lifestyle modification, and complementary therapies achieve superior outcomes compared to single-modality approaches.
Safety profiles for non-surgical treatments are excellent. Adverse events are rare and typically mild, making these approaches suitable for a wide range of patients including those with multiple comorbidities or high surgical risk.
Implementation and Treatment Protocols
Successful implementation of non-surgical heart blockage treatment requires systematic approach and comprehensive planning. Treatment protocols must be individualized based on specific patient needs and circumstances.
Initial Assessment Phase involves comprehensive evaluation including medical history, current symptoms, diagnostic testing, and lifestyle assessment. This information guides treatment selection and protocol design.
Treatment Planning incorporates multiple therapeutic modalities based on individual needs and preferences. Protocols typically combine EECP therapy, lifestyle modifications, nutritional interventions, and complementary treatments.
Monitoring and Adjustment ensures optimal treatment progression and allows for protocol modifications based on patient response and changing needs. Regular follow-up assessments track progress and guide treatment adjustments.
Patient Education components ensure understanding of treatment rationale, expected outcomes, and lifestyle requirements. Educated patients achieve better compliance and superior long-term results.
Support Systems including family involvement, group programs, and professional guidance help maintain treatment adherence and lifestyle changes. Social support significantly impacts treatment success and long-term outcomes.
Long-term Maintenance protocols help sustain treatment benefits and prevent disease progression. Ongoing lifestyle maintenance and periodic treatment sessions support continued cardiovascular health.
Future Directions and Emerging Therapies
The field of non-surgical cardiovascular treatment continues to evolve with emerging technologies and therapeutic approaches. Several promising developments offer enhanced treatment options for the future.
Advanced EECP Protocols incorporating personalized compression patterns and real-time physiological monitoring may enhance treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes. Technology improvements continue to refine this proven therapy.
Nutritional Genomics applications help identify individual nutritional needs based on genetic profiles. Personalized nutrition protocols may optimize cardiovascular healing and prevention strategies.
Regenerative Medicine approaches including stem cell therapies and growth factor treatments show promise for enhancing natural healing processes and promoting arterial regeneration.
Digital Health Integration utilizing wearable devices, remote monitoring, and artificial intelligence may improve treatment precision and patient engagement in therapeutic protocols.
Combination Therapy Optimization research continues to identify the most effective combinations of non-surgical treatments for various patient populations and disease severities.
These emerging approaches promise to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of non-surgical cardiovascular treatments while maintaining the safety and holistic benefits that characterize these therapeutic modalities.
About the Author
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a renowned clinical nutritionist and researcher specializing in EECP therapy and clinical nutrition. With extensive expertise in treating patients with lifestyle disorders, he has successfully treated over 25,000 heart and diabetes patients globally. As the founder of FIT MY HEART and consultant at NEXIN HEALTH and MD CITY Hospital Noida, Mr. Sengar combines evidence-based medicine with holistic healing approaches to provide comprehensive cardiovascular care. His dedication to non-invasive treatment modalities has helped countless patients achieve optimal heart health without surgical interventions.
Visit: www.viveksengar.in
💬 Need Expert Guidance for Your Health?
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a renowned Consultant and Clinical Nutritionist at NexIn Health with 13+ years of experience. He has helped over 25,000 patients recover from chronic diseases like diabetes, heart conditions, obesity, and metabolic disorders through evidence-based lifestyle therapy and nutrition.
🌿 NexIn Health is India’s Leading Integrated Wellness Center, specializing in:
-
Non-Surgical Heart Disease Treatments
-
Diabetes Reversal Programs
-
Pain Management
-
Obesity & Fatty Liver Management
-
Women’s Hormonal Health (PCOS, Menopause, etc.)
With a team of 25+ wellness coaches, doctors, clinical nutritionists, and researchers, and over 30 centers globally, NexIn Health combines modern science with natural, non-invasive healing methods — empowering patients to reclaim their health without surgery or lifelong medications.
🔗 Visit NexIn Health: www.nexinhealth.in
📞 Call or WhatsApp: +91 9310 14 5010
📩 Email: care@nexinhealth.in
✅ Whether you’re seeking a second opinion or want to reverse your health condition naturally — take the first step towards healing today.
Your health transformation begins with the right expert.
Connect Now. Live Better
Also Read: EECP Treatment in Noida
Heart Blockage Reversal with Plant Based Diet
Frequently Asked Questions: Natural Heart Blockage Treatment without Surgery
1. Can heart blockages be completely reversed without surgery?
Yes, research demonstrates that comprehensive lifestyle approaches can reverse arterial blockages. Dr. Dean Ornish’s studies show significant regression of coronary atherosclerosis through diet, exercise, stress management, and social support.
2. How effective is EECP treatment for heart blockages?
EECP therapy shows 70-85% success rates in symptom improvement. Most patients experience significant reduction in chest pain, improved exercise tolerance, and enhanced quality of life within 6-8 weeks of treatment.
3. What is the success rate of natural heart blockage treatment?
Natural treatment approaches achieve 70-80% success rates when properly implemented. Success depends on patient compliance, disease severity, and comprehensive protocol adherence.
4. Are there any risks associated with non-surgical heart treatments? Non-surgical treatments have minimal risks and excellent safety profiles. Side effects are rare and typically mild, making these approaches suitable for high-risk patients who cannot undergo surgery.
5. How long does it take to see results from natural heart treatments?
Initial improvements often occur within 2-4 weeks, with significant benefits typically seen within 6-12 weeks. Maximum benefits usually develop over 6-12 months of consistent treatment.
6. Can I stop my heart medications with natural treatment?
Medication adjustments should only be made under medical supervision. Many patients reduce medication needs as their condition improves, but changes must be carefully monitored by healthcare providers.
7. What dietary changes are most important for heart blockage reversal?
Plant-based diets rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes while avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive fats show the greatest benefit for arterial health.
8. Is exercise safe for people with heart blockages?
Appropriate exercise is beneficial and necessary for heart health. Exercise programs should be medically supervised and gradually progressive, starting with low-intensity activities.
9. How does stress affect heart blockages?
Chronic stress accelerates atherosclerotic progression through elevated cortisol levels and increased inflammation. Stress management is crucial for cardiovascular healing and prevention.
10. Can Ayurveda cure heart blockages?
Ayurvedic treatments support cardiovascular health and can be effective components of comprehensive treatment protocols. Therapies like Hriday Basti and specific herbal formulations provide significant benefits.
11. What role do detox drinks play in heart health?
Specific detox drinks provide antioxidants, anti-inflammatory compounds, and nutrients that support cardiovascular healing. Green tea, pomegranate juice, and turmeric preparations offer particular benefits.
12. Is fasting safe for heart patients?
Therapeutic fasting can benefit cardiovascular health when properly supervised. Intermittent fasting and modified fasting approaches are generally safe for most heart patients with appropriate medical guidance.
13. How often should EECP treatments be repeated?
Initial EECP protocols typically involve 35 – 40
sessions over 7 weeks. Maintenance sessions may be recommended annually or as needed based on individual response and symptoms.
14. Can homeopathy help with heart blockages?
Homeopathic remedies can support cardiovascular health as part of comprehensive treatment. Constitutional prescribing addresses individual symptom patterns and supports natural healing processes.
15. What is the long-term outlook for natural heart treatment?
Long-term outcomes are excellent with proper lifestyle maintenance. Many patients maintain improved cardiovascular health for years and experience continued benefits with sustained lifestyle practices.