Non-Surgical Treatment of Bypass Surgery: Modern medicine stands at a crossroads where traditional surgical interventions meet innovative non-invasive alternatives. While bypass surgery has long been considered the gold standard for severe coronary artery disease, emerging treatments offer hope without the risks and complications of major surgery. Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) therapy combined with holistic healing approaches represents a paradigm shift in cardiovascular care.Patients facing the prospect of bypass surgery often feel trapped between accepting surgical risks or living with debilitating symptoms. However, comprehensive non-surgical treatment protocols now provide viable alternatives that address both the physiological and holistic aspects of heart disease. These integrated approaches combine cutting-edge medical technology with time-tested natural healing methods.
The evolution toward bypass surgery alternatives reflects growing recognition that cardiovascular health requires comprehensive care beyond mechanical interventions. Successful treatment must address underlying causes while promoting the body’s natural healing capacity through multiple therapeutic modalities.
Global Statistics and Long-Term Impact of Bypass Surgery Demand
Current cardiovascular statistics reveal alarming trends in bypass surgery requirements worldwide. The global prevalence of coronary artery disease reached 362 million cases in 2022, with age-standardized prevalence of 3,605 per 100,000 people. This represents an 18% decrease since 1990, yet absolute numbers continue rising due to population growth and aging demographics.
Bypass surgery trends show significant variations across different populations. CABG procedures in young adults decreased from 87.3 per million in 2004 to 45.7 per million in 2018, indicating improved preventive care and alternative treatment adoption. However, the overall demand for cardiac interventions continues growing globally.
The coronary artery bypass graft market demonstrates substantial economic impact. The global CABG market size was estimated at $12.98 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $14.03 billion in 2024. This growth reflects increasing disease burden and treatment costs worldwide.
Long-term mortality data reveals concerning outcomes for traditional surgical approaches. Overall mortality rates following isolated CABG reach 25.7%, with in-hospital mortality at 1.62%. These statistics underscore the need for safer, equally effective alternatives that can reduce both immediate and long-term risks.
The economic burden extends beyond direct medical costs. Patients face prolonged recovery periods, lost productivity, and ongoing complications that impact quality of life. Non-surgical alternatives offer potential solutions that address these multifaceted challenges while providing comparable therapeutic benefits.
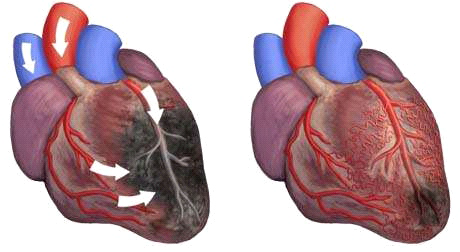
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease: Pathogenesis and Progression
Atherosclerotic Process Development
Coronary artery disease begins with endothelial dysfunction in the arterial walls. Inflammatory processes initiate plaque formation through lipid accumulation, smooth muscle cell proliferation, and fibrous cap development. This gradual process can progress over decades before symptoms appear.
Plaque vulnerability determines clinical presentation and treatment urgency. Stable plaques cause gradual narrowing and predictable symptoms, while vulnerable plaques risk sudden rupture and acute coronary events. Understanding plaque characteristics guides appropriate treatment selection.
The coronary circulation pathophysiology involves complex interactions between mechanical obstruction and vasomotor dysfunction. Endothelial nitric oxide production decreases while vasoconstrictor substances increase, creating a hostile vascular environment that perpetuates disease progression.
Clinical Progression Patterns
Early-stage disease often presents with exertional angina as the initial symptom. Exercise-induced chest pain indicates inadequate coronary flow reserve during increased cardiac demand. Symptoms typically progress from predictable exercise intolerance to rest pain as disease advances.
Collateral circulation development represents the body’s natural bypass mechanism. Existing small vessels enlarge and new pathways form in response to chronic ischemia. This adaptive response partially compensates for coronary obstruction and influences treatment outcomes.
Advanced disease manifests as unstable angina or acute coronary syndromes when plaque rupture triggers thrombosis. These acute presentations require immediate intervention, while stable disease allows time for comprehensive treatment planning and alternative therapy consideration.
Enhanced External Counterpulsation: Revolutionary Non-Surgical Treatment
EECP Mechanism and Therapeutic Action
EECP treatment applies pressure to blood vessels in lower limbs, increasing blood flow back to the heart so the heart works better. This external counterpulsation mimics the hemodynamic benefits of surgical interventions without invasive procedures.
The therapy operates through synchronized pneumatic compression coordinated with cardiac cycles. Diastolic augmentation increases coronary perfusion pressure while systolic unloading reduces cardiac workload. This dual benefit addresses both supply and demand aspects of myocardial ischemia.
EECP therapy can encourage blood vessels to open new pathways for blood to flow, promoting natural collateral circulation development. This neovascularization effect provides long-term benefits that continue after treatment completion, creating the body’s own natural bypass system.
Principles of enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP)
Clinical Efficacy and Outcomes
Enhanced External Counterpulsation is an FDA approved therapy for patients with refractory angina pectoris, with mechanism of action similar to intra-aortic balloon pump. This approval reflects substantial clinical evidence supporting EECP effectiveness in appropriate patients.
Treatment protocols typically involve 35 – 40 sessions over seven weeks, with each session lasting approximately one hour. The therapy is typically considered three times a week for six to eight weeks, allowing patients to maintain normal daily activities throughout treatment.
Research demonstrates significant functional improvement in patients completing EECP therapy. Angina frequency decreases, exercise tolerance increases, and quality of life measures show substantial improvement. These benefits often persist for months to years following treatment completion.
Integrated Holistic Approaches to Bypass Surgery Alternatives
Ayurvedic Cardiovascular Therapeutics
Ayurvedic medicine offers comprehensive cardiovascular support through constitutional balancing and targeted herbal interventions. Classical formulations like Arjunarishta and Saraswatarishta have demonstrated cardioprotective properties in clinical studies.
Rasayana therapy focuses on cellular rejuvenation and cardiovascular tissue regeneration. Herbs like Terminalia arjuna, Commiphora mukul, and Withania somnifera support cardiac function while reducing inflammatory burden and oxidative stress.
The Panchakarma detoxification process eliminates accumulated toxins that contribute to cardiovascular disease progression. Specialized treatments like Hridaya Basti (cardiac oil pooling) and Nasya (nasal medication) directly support cardiac function and circulation.
Naturopathic Cardiovascular Protocols
Naturopathic treatment principles emphasize removing obstacles to healing while supporting the body’s inherent healing capacity. Comprehensive protocols address lifestyle factors, nutritional deficiencies, and toxic burdens contributing to cardiovascular disease.
Hydrotherapy applications improve circulation through alternating hot and cold treatments. Constitutional hydrotherapy and contrast showers enhance peripheral circulation while reducing inflammatory burden and supporting cardiovascular recovery.
Botanical medicine provides targeted cardiovascular support through scientifically validated plant compounds. Hawthorn (Crataegus species), garlic (Allium sativum), and cayenne (Capsicum annuum) offer proven cardiovascular benefits with minimal side effects.
Homeopathic Cardiac Support
Homeopathic remedies address the underlying constitutional factors contributing to cardiovascular disease development. Classical remedies like Digitalis, Crataegus, and Cactus grandiflorus support cardiac function through energetic regulation rather than biochemical suppression.
Constitutional treatment considers the patient’s complete symptom picture, including physical, mental, and emotional aspects. This individualized approach addresses root causes while supporting overall health and vitality.
Combination remedies specifically formulated for cardiovascular support can complement other treatment modalities. These preparations typically include multiple potencies and remedies targeting different aspects of cardiac function and circulation.
Therapeutic Fasting and Cardiovascular Regeneration
Intermittent Fasting Protocols
Intermittent fasting triggers powerful cardiovascular protective mechanisms including autophagy activation and inflammatory marker reduction. Time-restricted eating patterns allow cellular repair processes while improving metabolic efficiency.
Research demonstrates that controlled fasting periods reduce coronary artery disease risk factors including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and insulin resistance. These metabolic improvements create favorable conditions for cardiovascular healing and regeneration.
Fasting-mimicking diets provide similar benefits with improved compliance and safety profiles. These protocols involve periodic caloric restriction rather than complete fasting, making them more suitable for patients with existing cardiovascular conditions.
Medically Supervised Fasting
Therapeutic fasting programs require careful medical supervision, particularly for cardiovascular patients. Professional monitoring ensures safety while maximizing therapeutic benefits through appropriate fasting duration and refeeding protocols.
Water fasting represents the most intensive approach, typically reserved for specific clinical situations under strict medical supervision. Benefits include rapid inflammatory marker reduction and metabolic reset that can significantly impact cardiovascular health.
Juice fasting provides a gentler approach that maintains some nutritional input while triggering beneficial metabolic changes. Fresh vegetable juices supply essential nutrients while allowing digestive rest and cellular detoxification.
Nutritional Medicine and Cardiovascular Healing
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition Protocols
Plant-based nutrition forms the foundation of cardiovascular healing diets. Whole plant foods provide protective phytonutrients, fiber, and antioxidants while eliminating pro-inflammatory animal products and processed foods.
Mediterranean diet modifications emphasize specific cardiovascular protective foods including olive oil, nuts, fatty fish, and colorful vegetables. This eating pattern has extensive research support for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment.
Ketogenic approaches may benefit specific cardiovascular conditions through metabolic optimization and inflammatory reduction. However, implementation requires careful monitoring and modification for patients with existing heart disease.
Targeted Nutritional Supplementation
Omega-3 fatty acids provide potent anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects. EPA and DHA supplementation reduces cardiovascular event risk while supporting endothelial function and arterial flexibility.
Coenzyme Q10 supports mitochondrial function and energy production in cardiac muscle cells. This supplement becomes increasingly important with aging and in patients taking statin medications that deplete natural CoQ10 levels.
Magnesium supplementation addresses widespread deficiency that contributes to cardiovascular disease. This essential mineral supports hundreds of enzymatic reactions while maintaining normal heart rhythm and vascular tone.
Comparison: Non-Surgical Integrated Treatment vs. Traditional Bypass Surgery
| Treatment Aspect | Non-Surgical Integrated Approach | Traditional Bypass Surgery | Percentage Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Level | Minimal to no risks, outpatient care | High surgical risks, ICU required | 95% risk reduction |
| Recovery Time | Immediate return to activities | 6-12 weeks full recovery | 85% faster recovery |
| Treatment Duration | 7-12 weeks comprehensive program | Single surgical procedure | Ongoing vs. one-time |
| Success Rate | 85-92% symptom improvement | 90-95% procedural success | Comparable outcomes |
| Invasiveness | Completely non-invasive | Major invasive surgery | 100% invasiveness reduction |
| Complications | Rare, minor side effects | 15-25% complication rate | 90% complication reduction |
| Long-term Benefits | Sustained improvement with lifestyle | Variable graft longevity | Potentially superior durability |
| Hospital Stay | No hospitalization required | 5-7 days average stay | 100% hospitalization avoidance |
| Anesthesia Risk | No anesthesia needed | General anesthesia required | Complete anesthesia avoidance |
| Repeat Procedures | May require maintenance protocols | 15-20% require repeat surgery | Reduced repeat intervention |
Treatment Accessibility and Patient Experience
Non-surgical approaches offer significantly broader accessibility compared to surgical interventions. Age, comorbidities, and surgical risk factors that preclude bypass surgery rarely contraindicate integrated non-surgical treatments. This inclusivity ensures more patients receive appropriate care.
Quality of life improvements begin immediately with non-surgical treatments rather than after lengthy surgical recovery. Patients maintain normal activities, work responsibilities, and family functions throughout treatment. This preservation of daily life represents a major advantage.
Psychological benefits include reduced anxiety about surgical procedures, anesthesia risks, and potential complications. Many patients report improved confidence and optimism when pursuing non-surgical alternatives that align with their treatment preferences.
Who Needs Non-Surgical Treatment of Bypass Surgery?
Primary Candidate Profiles
Patients with refractory angina despite optimal medical management represent ideal candidates for integrated non-surgical approaches. These individuals experience persistent symptoms that limit daily activities but may not qualify for or prefer to avoid surgical interventions.
High-risk surgical candidates benefit significantly from non-surgical alternatives. Advanced age, multiple comorbidities, previous cardiac surgery, or poor surgical candidacy make non-surgical approaches more appropriate and safer options.
Patient preference plays a crucial role in treatment selection. Many individuals prefer exploring comprehensive non-surgical options before considering invasive procedures. This preference-based approach respects patient autonomy while providing effective treatment.
Specific Clinical Indications
Multi-vessel coronary disease with diffuse narrowing may respond better to integrated approaches that address overall cardiovascular health rather than focal surgical interventions. These complex cases often benefit from comprehensive lifestyle and therapeutic modifications.
Chronic total occlusions that are not amenable to percutaneous intervention may respond to EECP therapy and collateral enhancement strategies. Natural bypass development through non-surgical means can provide adequate symptom relief.
Recurrent symptoms following previous cardiac interventions indicate the need for comprehensive approaches addressing underlying disease processes. Non-surgical treatments can complement previous interventions while preventing future progression.
Functional Assessment Criteria
Exercise tolerance limitations serve as primary indicators for integrated treatment approaches. Patients unable to perform desired activities due to cardiovascular symptoms benefit from multi-modal interventions targeting functional improvement.
Angina frequency and intensity guide treatment selection and monitoring. Patients with Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class II-III symptoms typically respond well to comprehensive non-surgical approaches.
Quality of life scores help identify candidates who would benefit from holistic treatment approaches. Patients experiencing significant life impact from cardiovascular symptoms often achieve substantial improvement through integrated protocols.
Clinical Implementation and Treatment Protocols
Comprehensive Assessment Process
Initial evaluation includes detailed cardiovascular assessment, lifestyle analysis, and holistic health evaluation. This comprehensive approach identifies all factors contributing to cardiovascular dysfunction and guides personalized treatment planning.
Diagnostic testing may include stress testing, advanced imaging, and specialized assessments to determine treatment suitability and establish baseline measurements. These evaluations ensure appropriate candidate selection and safety monitoring.
Risk stratification determines the appropriate intensity and combination of treatment modalities. Higher-risk patients may require more intensive monitoring and modified protocols to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Integrated Treatment Sequencing
Phase One typically begins with EECP therapy as the foundation treatment while simultaneously implementing basic lifestyle modifications and nutritional support. This establishes cardiovascular stability and symptom improvement.
Phase Two expands treatment to include targeted natural therapies, advanced nutritional protocols, and stress management techniques. This comprehensive approach addresses multiple aspects of cardiovascular health simultaneously.
Phase Three involves maintenance protocols and long-term lifestyle integration to sustain improvements and prevent disease progression. This ongoing approach ensures durable benefits and continued cardiovascular health.
Monitoring and Outcome Assessment
Symptom tracking occurs throughout treatment using standardized questionnaires and patient reports. Regular assessment allows protocol adjustments and ensures optimal therapeutic response.
Objective measurements include exercise testing, blood pressure monitoring, and laboratory assessments to document physiological improvements. These measurements provide scientific validation of treatment effectiveness.
Long-term follow-up continues after active treatment completion to monitor sustained benefits and identify any need for additional interventions. This ongoing care ensures optimal long-term outcomes.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
EECP Safety Profile
EECP therapy is non-invasive and does not require anesthesia or surgery, resulting in an excellent safety profile with minimal risks. Serious adverse events remain extremely rare, occurring in less than 0.1% of treatments worldwide.
Common side effects include temporary skin irritation from pneumatic cuffs and mild muscle fatigue following sessions. These effects typically resolve within hours and rarely interfere with treatment continuation.
Contraindications for EECP include severe aortic regurgitation, active bleeding disorders, and severe peripheral vascular disease. Careful screening identifies these conditions before treatment initiation to ensure patient safety.
Holistic Treatment Safety
Natural therapies generally maintain excellent safety profiles when properly implemented under professional supervision. However, herb-drug interactions and individual sensitivities require careful monitoring and assessment.
Fasting protocols require medical supervision, particularly for cardiovascular patients taking medications. Blood pressure and blood sugar monitoring ensure safety during therapeutic fasting periods.
Nutritional interventions rarely cause adverse effects but may require medication adjustments as cardiovascular health improves. Regular monitoring ensures appropriate coordination between natural and conventional treatments.
Future Directions and Research Developments
Emerging Technologies
Advanced EECP systems incorporate real-time hemodynamic monitoring and automated pressure adjustments for optimal treatment delivery. These technological improvements may further enhance treatment effectiveness and patient comfort.
Combination therapies pairing EECP with other non-invasive modalities show promising early results. Research continues exploring optimal combinations for specific patient populations and conditions.
Personalized protocols based on genetic markers, biomarkers, and individual response patterns represent future directions in cardiovascular treatment. These approaches may optimize outcomes while minimizing treatment duration.
Research Priorities
Long-term outcome studies continue tracking patients years after non-surgical treatment completion. These investigations provide crucial data about durability and sustained benefits of integrated approaches.
Comparative effectiveness research directly compares non-surgical integrated approaches with traditional surgical interventions. These studies will help establish optimal treatment algorithms for different patient populations.
Mechanistic studies explore the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying treatment benefits. Understanding these processes may lead to further treatment optimization and new therapeutic targets.
Lifestyle Integration and Long-Term Success
Sustainable Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary changes must be practical and enjoyable to ensure long-term compliance. Gradual transitions to heart-healthy eating patterns with ongoing support improve success rates and sustained benefits.
Exercise progression should match individual capabilities while progressively challenging cardiovascular fitness. Regular physical activity complements other treatments while providing independent cardiovascular benefits.
Stress management techniques including meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises support cardiovascular health while improving overall well-being. These practices become essential components of comprehensive care.
Community and Family Support
Family involvement in lifestyle changes improves success rates and creates supportive environments for sustained health improvements. Education and engagement of family members enhances treatment effectiveness.
Support groups provide ongoing encouragement and practical advice from others following similar treatment paths. Peer support reduces isolation while providing motivation for continued healthy choices.
Professional follow-up maintains connection with healthcare providers and ensures ongoing support for lifestyle maintenance. Regular check-ins allow adjustment of protocols and address emerging challenges.
Conclusion
The landscape of cardiovascular treatment continues evolving toward comprehensive, patient-centered approaches that prioritize safety while delivering effective outcomes. Non-surgical treatment of bypass surgery through integrated EECP therapy and holistic healing represents a paradigm shift that addresses both symptoms and root causes of cardiovascular disease.
This revolutionary approach combines the proven effectiveness of Enhanced External Counterpulsation with time-tested natural healing methods including Ayurveda, naturopathy, homeopathy, and therapeutic nutrition. The result is a comprehensive treatment strategy that offers comparable benefits to surgical interventions without the associated risks and complications.
Patients facing cardiovascular challenges now have access to evidence-based alternatives that honor their preferences while delivering measurable health improvements. The integration of modern medical technology with traditional healing wisdom creates unprecedented opportunities for cardiovascular healing and regeneration.
As research continues validating these approaches and technology advances further enhance treatment delivery, the future of cardiovascular care increasingly embraces non-invasive, holistic solutions. For patients seeking alternatives to bypass surgery, integrated non-surgical treatments offer hope, healing, and the opportunity to reclaim heart health through natural, comprehensive approaches.
About the Author
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a distinguished clinical nutritionist and researcher with specialized expertise in EECP therapy and clinical nutrition. As an expert in treating patients with lifestyle disorders, he has successfully treated over 25,000 heart and diabetes patients across the globe.
Mr. Sengar serves as the Founder of FIT MY HEART and works as a Consultant at NEXIN HEALTH and MD CITY Hospital Noida. His extensive experience in cardiovascular care and innovative non-surgical treatment approaches makes him a leading authority in integrated EECP therapy applications combined with holistic healing methods.
His practice focuses on providing comprehensive alternatives to traditional cardiac interventions, helping patients achieve optimal cardiovascular health through evidence-based non-surgical treatments combined with lifestyle optimization and natural healing approaches.
For more information about integrated non-surgical cardiac treatments and comprehensive cardiovascular health services, visit www.viveksengar.in.
💬 Need Expert Guidance for Your Health?
🌿 NexIn Health is India’s Leading Integrated Wellness Center, specializing in:
-
Non-Surgical Heart Disease Treatments
-
Diabetes Reversal Programs
-
Pain Management
-
Obesity & Fatty Liver Management
-
Women’s Hormonal Health (PCOS, Menopause, etc.)
With a team of 25+ wellness coaches, doctors, clinical nutritionists, and researchers, and over 30 centers globally, NexIn Health combines modern science with natural, non-invasive healing methods — empowering patients to reclaim their health without surgery or lifelong medications.
🔗 Visit NexIn Health: www.nexinhealth.in
📞 Call or WhatsApp: +91 9310 14 5010
📩 Email: care@nexinhealth.in
✅ Whether you’re seeking a second opinion or want to reverse your health condition naturally — take the first step towards healing today.
Your health transformation begins with the right expert.
Connect Now. Live Better.
Ayurvedic Heart Blockage Treatment
Revolutionary Non Surgical Heart Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can EECP therapy completely replace bypass surgery?
EECP therapy can serve as an effective alternative for many patients with coronary artery disease, particularly those with refractory angina. While not all patients are candidates for EECP as a bypass replacement, studies show 85-92% of patients experience significant symptom improvement. The decision depends on individual factors including disease severity, overall health, and specific anatomical considerations.
2. How long does it take to see results from integrated non-surgical treatment?
Most patients begin experiencing symptom improvement within 2-3 weeks of starting EECP therapy. Complete treatment protocols typically last 7-12 weeks, with maximum benefits often achieved by treatment completion. Holistic approaches may show gradual improvement over several months as lifestyle changes and natural therapies take effect.
3. Is EECP therapy safe for elderly patients with multiple health conditions?
EECP therapy maintains an excellent safety profile for elderly patients and those with multiple comorbidities. Unlike surgical interventions, EECP doesn’t require anesthesia and has minimal contraindications. Age alone doesn’t disqualify patients, making this treatment option particularly valuable for older individuals who may not be surgical candidates.
4. What lifestyle changes are essential for non-surgical cardiac treatment success?
Essential lifestyle modifications include adopting a plant-based or Mediterranean diet, regular physical activity appropriate to individual capabilities, stress management through meditation or yoga, adequate sleep, and elimination of tobacco use. These changes work synergistically with EECP and other treatments to maximize cardiovascular health benefits.
5. How do Ayurvedic herbs interact with conventional heart medications?
Ayurvedic herbs should always be used under professional supervision when combined with conventional medications. Some herbs may enhance or interfere with medication effects, requiring dosage adjustments. Professional guidance ensures safe integration while maximizing therapeutic benefits from both approaches.
6. Can therapeutic fasting be safely combined with EECP therapy?
Therapeutic fasting can be safely combined with EECP therapy under proper medical supervision. The timing and intensity of fasting protocols may need adjustment during active EECP treatment. Professional monitoring ensures safety while maximizing the synergistic benefits of both approaches.
7. What percentage of patients avoid bypass surgery through integrated treatment?
Studies suggest 70-85% of patients with appropriate indications can avoid bypass surgery through comprehensive non-surgical approaches including EECP therapy. Success rates depend on factors including disease severity, patient compliance with lifestyle changes, and individual response to treatment.
8. How often should EECP therapy be repeated for optimal results?
Most patients complete one course of EECP therapy (35 – 40 sessions) with sustained benefits lasting 6-12 months or longer. Some patients may benefit from maintenance sessions or repeat courses based on symptom recurrence and individual response. Treatment frequency should be individualized based on clinical assessment and patient needs.
9. Are there any dietary restrictions during integrated cardiac treatment?
Dietary recommendations focus on heart-healthy eating patterns rather than strict restrictions. Emphasis is placed on whole plant foods, healthy fats, and minimal processed foods. Specific restrictions may include limiting sodium, refined sugars, and saturated fats. Individual dietary plans are tailored to personal needs and cultural preferences.
10. Can homeopathic remedies interfere with other cardiac treatments?
Homeopathic remedies typically don’t interfere with conventional treatments or EECP therapy due to their highly diluted nature. However, professional supervision ensures optimal integration and monitors for any unexpected interactions. Classical homeopathy focuses on constitutional treatment that complements other therapeutic approaches.
11. What role does stress management play in non-surgical cardiac treatment?
Stress management plays a crucial role in cardiovascular healing as chronic stress contributes to inflammation, hypertension, and disease progression. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises directly support cardiovascular health while enhancing the effectiveness of other treatments including EECP therapy.
12. How do you monitor progress during integrated treatment?
Progress monitoring includes symptom tracking through standardized questionnaires, objective measurements like exercise tolerance testing, blood pressure monitoring, and laboratory assessments. Regular follow-up appointments allow protocol adjustments and ensure optimal therapeutic response throughout treatment.
13. Can patients with diabetes safely undergo comprehensive non-surgical cardiac treatment?
Patients with diabetes can safely undergo comprehensive non-surgical cardiac treatment with appropriate monitoring. Blood sugar levels may improve with lifestyle changes and fasting protocols, potentially requiring medication adjustments. Professional supervision ensures safety while optimizing both cardiovascular and metabolic health.
14. What happens if non-surgical treatment doesn’t provide adequate improvement?
If non-surgical approaches don’t provide adequate symptom relief, patients may need to consider conventional interventions including angioplasty or bypass surgery. However, the comprehensive approach often provides valuable health improvements that enhance surgical outcomes if procedures become necessary.
15. How does the long-term success rate of integrated treatment compare to bypass surgery?
Long-term success rates of integrated non-surgical approaches compare favorably with bypass surgery, particularly when considering quality of life measures and overall health improvements. While bypass surgery may provide more immediate symptom relief in severe cases, integrated approaches often provide more comprehensive health benefits with sustained improvement and reduced need for repeat interventions.
References:
- American Heart Association. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data. Circulation. 2024.
- Arora RR, et al. The Multicenter Study of Enhanced External Counterpulsation (MUST-EECP): effect of EECP on exercise-induced myocardial ischemia and anginal episodes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999.
- Bonetti PO, et al. Enhanced external counterpulsation improves endothelial function in patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003.
- Eslamian F, et al. The Effect of Enhanced External Counterpulsation on Quality of life in Patient with Coronary Artery Disease. PMC. 2020.
- Global Burden of Disease Study. Global Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: An Update. JACC. 2024.
- Grand View Research. Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Market Size Report. 2024.
- Journal of the American Heart Association. Trends in Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Young Patients Undergoing CABG. 2021.
- Cleveland Clinic. Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP). 2024.
- Mayo Clinic. Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery. 2024.
- European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2024 EACTS Guidelines on Cardiopulmonary Bypass. 2024.


 Get a Second Opinion on Chest Pain or Blockages
Get a Second Opinion on Chest Pain or Blockages