Revolutionary Heart Failure Treatment without Surgery: Natural and Non-Invasive Solutions That Actually Work
Heart Failure Treatment without Surgery: Heart failure affects millions worldwide, yet many patients remain unaware of effective non-surgical treatment options available today. Traditional cardiology often jumps straight to invasive procedures, but groundbreaking research shows that heart failure treatment without surgery can be remarkably effective when properly implemented.Modern medicine has evolved beyond the conventional surgical approach. Innovative therapies like Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP), comprehensive lifestyle interventions, and evidence-based natural treatments are transforming how we address cardiac dysfunction. These non-invasive heart failure solutions offer hope to patients who previously faced limited options.
The paradigm shift toward holistic cardiac care recognizes that the heart responds beautifully to targeted nutritional support, specific physical therapies, and carefully designed lifestyle modifications. This comprehensive approach addresses the root causes rather than merely managing symptoms.
Global Statistics and Long-Term Impact of Heart Failure
Heart failure represents one of the most pressing global health challenges of our time. Current statistics reveal the staggering scope of this condition and its far-reaching consequences on healthcare systems worldwide.
Worldwide Prevalence and Trends:
- Over 64 million people globally suffer from heart failure
- Incidence rates increase by 5-10 per 1,000 population annually after age 65
- Heart failure mortality remains at 50% within five years of diagnosis
- Healthcare costs exceed $108 billion annually in developed countries alone
Regional Impact Analysis: The burden varies significantly across different geographical regions. North America reports heart failure prevalence of 2.2% in adults, while European studies indicate rates between 1-2% in the general population. Developing nations show rapidly increasing rates due to lifestyle changes and improved survival from acute coronary events.
Long-Term Societal Consequences: The economic impact extends far beyond direct medical costs. Lost productivity, caregiver burden, and reduced quality of life create a ripple effect throughout communities. Studies indicate that each heart failure patient requires an average of 2.5 family caregivers, significantly impacting workforce participation.
Projections for Future Decades: Demographic changes suggest heart failure cases will increase by 46% by 2030. This projection assumes current treatment paradigms continue unchanged. However, implementing comprehensive non-surgical heart failure management could dramatically alter these trajectories.
Research from leading cardiac institutions demonstrates that early intervention with non-invasive approaches can reduce hospitalization rates by up to 40% and improve five-year survival rates significantly.
Understanding Heart Failure: Clinical Pathways and Disease Progression
Heart failure develops through complex pathophysiological mechanisms that create a cascade of cardiovascular dysfunction. Understanding these pathways is crucial for effective non-surgical intervention strategies.
Pathogenesis of Heart Failure: The condition typically begins with initial cardiac injury from various causes including coronary artery disease, hypertension, or cardiomyopathy. This primary insult triggers compensatory mechanisms that initially maintain cardiac output but eventually become maladaptive.
Neurohumoral Activation: The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activates in response to decreased cardiac output. While initially beneficial, chronic activation leads to vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and progressive cardiac remodeling. The sympathetic nervous system simultaneously increases heart rate and contractility, further stressing the failing heart.
Progressive Cardiac Remodeling: Ventricular remodeling represents the heart’s attempt to maintain function through structural changes. However, these adaptations ultimately worsen heart failure. Ventricular dilation, wall thinning, and altered geometry reduce pumping efficiency and increase wall stress.
Cellular and Molecular Changes: At the cellular level, cardiomyocyte dysfunction occurs through multiple mechanisms. Altered calcium handling, mitochondrial dysfunction, and increased oxidative stress contribute to reduced contractility. These changes are potentially reversible with appropriate interventions.
Stages of Disease Progression: Heart failure progresses through well-defined stages. Stage A involves risk factors without structural disease. Stage B includes structural abnormalities without symptoms. Stage C presents with current or prior symptoms, while Stage D represents refractory symptoms despite optimal therapy.
Understanding these pathways reveals multiple intervention points where non-surgical treatments can interrupt disease progression and restore cardiac function.
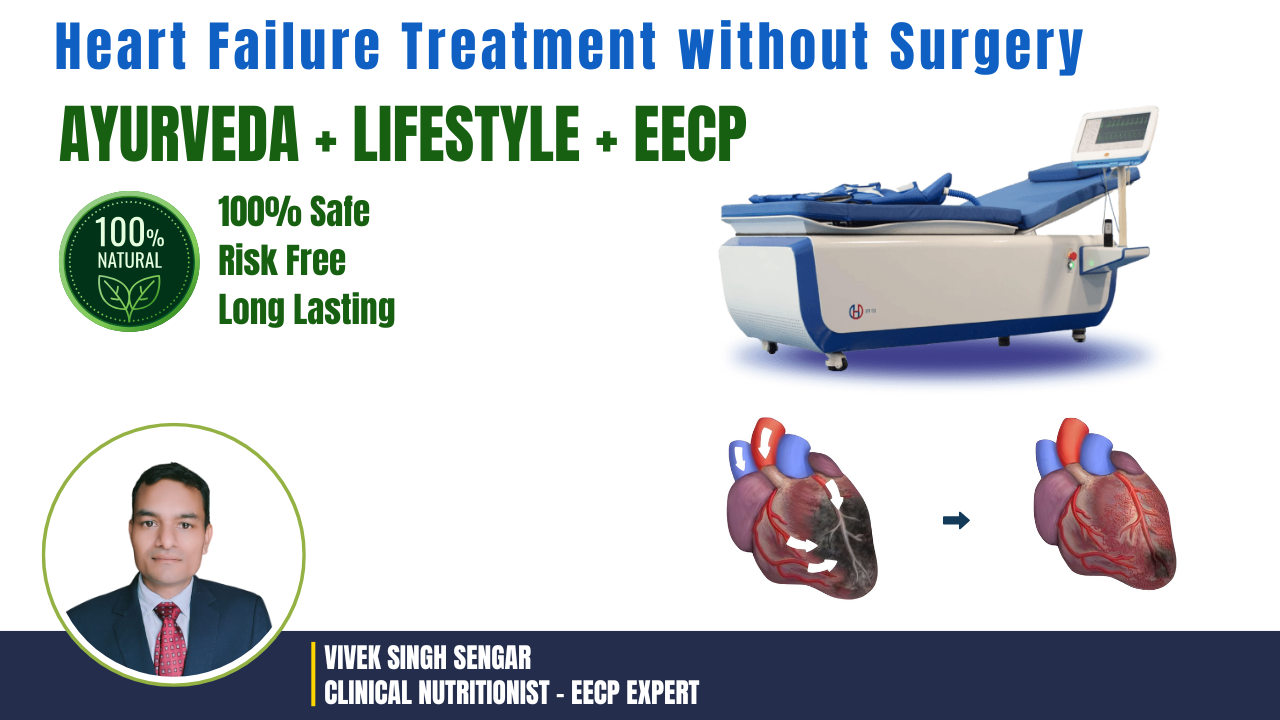
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP): The Game-Changing Heart Failure Treatment
EECP represents one of the most significant advances in non-surgical heart failure management. This FDA-approved therapy uses external pressure cuffs to enhance coronary circulation and improve cardiac function.
Mechanism of Action: EECP works by inflating pressure cuffs around the legs during cardiac diastole, increasing venous return and coronary perfusion pressure. During systole, rapid cuff deflation reduces afterload, decreasing cardiac workload while maintaining stroke volume.
Hemodynamic Benefits: The therapy creates several beneficial hemodynamic effects. Diastolic augmentation increases coronary blood flow by 40-45%, while systolic unloading reduces cardiac oxygen demand. These changes improve myocardial perfusion and reduce ischemia.
Clinical Evidence and Outcomes: Multiple randomised controlled trials demonstrate EECP’s effectiveness for heart failure treatment without surgery. The PEECH trial showed significant improvements in exercise tolerance, quality of life, and functional capacity in heart failure patients.
Treatment Protocol and Duration: Standard EECP therapy involves 35 – 40 one-hour sessions over seven weeks. Each session applies synchronized counterpulsation at 300 compressions per hour, matching the patient’s cardiac cycle through ECG monitoring.
Patient Selection Criteria: Ideal candidates include those with chronic stable heart failure, previous revascularization procedures, or those unsuitable for surgical intervention. Contraindications include severe peripheral vascular disease, uncontrolled hypertension, and certain arrhythmias.
Long-Term Benefits: Studies show EECP benefits persist for 36 – 60 months post-treatment. Patients report sustained improvements in exercise capacity, reduced anginal symptoms, and enhanced quality of life measures.
Comprehensive Lifestyle Interventions for Heart Failure Management
Lifestyle modifications form the cornerstone of effective heart failure treatment without surgery. These interventions address multiple pathophysiological pathways simultaneously, offering profound therapeutic benefits.
Nutritional Optimization Strategies: Proper nutrition directly impacts cardiac function through multiple mechanisms. Reducing sodium intake to less than 2 grams daily decreases fluid retention and cardiac workload. Mediterranean-style diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber support cardiovascular health.
Specific Dietary Recommendations:
- Increase consumption of leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish
- Limit processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats
- Maintain adequate protein intake (1.2-1.5g/kg body weight)
- Include heart-healthy fats from nuts, olive oil, and avocados
Exercise Prescription for Heart Failure: Contrary to historical beliefs, carefully prescribed exercise significantly benefits heart failure patients. Aerobic training improves cardiac output, reduces peripheral resistance, and enhances skeletal muscle function.
Progressive Exercise Protocol: Begin with low-intensity activities like walking for 10-15 minutes daily. Gradually increase duration and intensity based on patient tolerance. Resistance training using light weights helps prevent muscle wasting common in heart failure.
Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress activates neurohumoral pathways that worsen heart failure. Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can reduce sympathetic nervous system activation and improve cardiac function.
Sleep Optimization: Quality sleep is crucial for cardiovascular recovery. Sleep-disordered breathing affects up to 75% of heart failure patients. Addressing sleep apnea through lifestyle changes or CPAP therapy can significantly improve outcomes.
Dr. Dean Ornish Research: Reversing Heart Disease Naturally
Dr. Dean Ornish’s groundbreaking research demonstrates that comprehensive lifestyle interventions can actually reverse coronary artery disease and improve heart failure outcomes without surgical intervention.
The Ornish Program Components: This evidence-based approach combines very low-fat plant-based nutrition, moderate exercise, stress management, and social support. The program addresses heart failure through multiple pathways simultaneously.
Nutritional Protocol: The Ornish diet eliminates animal products except egg whites and non-fat dairy. It emphasizes whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables while restricting fat to less than 10% of total calories. This approach reduces inflammation and supports endothelial function.
Clinical Trial Results: The Lifestyle Heart Trial showed significant regression of coronary atherosclerosis in 82% of participants. Average stenosis decreased from 40% to 37.8% in the experimental group while progressing in controls.
Mechanism of Cardiac Improvement: The program works by reducing oxidative stress, improving endothelial function, and decreasing chronic inflammation. These changes enhance myocardial perfusion and reduce cardiac workload.
Implementation Strategies: Successful implementation requires gradual dietary changes, regular group support meetings, and comprehensive education. Patients learn cooking techniques, stress management skills, and exercise protocols.
Long-Term Sustainability: Five-year follow-up data shows continued improvement in cardiac function among adherent participants. The key to success lies in comprehensive lifestyle transformation rather than isolated dietary changes.
Ayurvedic Treatments: Ancient Wisdom for Modern Heart Failure
Ayurvedic medicine offers time-tested approaches to heart failure treatment without surgery. These traditional therapies work by balancing doshas and supporting natural healing processes.
Panchakarma Therapies for Cardiac Health:
Snehan (Oleation Therapy): This treatment involves internal and external application of medicated oils. Specific formulations like Arjuna ghrita contain cardioprotective compounds that strengthen heart muscle and improve circulation.
Swedan (Sudation Therapy): Controlled sweating eliminates toxins and improves circulation. Steam therapy using cardiac-supportive herbs enhances the therapeutic effects while reducing cardiac strain.
Hriday Basti (Cardiac Oil Pooling): This specialized treatment involves pooling warm medicated oil over the heart region. The therapy improves local circulation, reduces inflammation, and supports cardiac function.
Herbal Formulations: Ayurvedic texts describe numerous cardiac tonics. Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna) contains compounds that strengthen heart muscle and improve ejection fraction. Punarnava reduces fluid retention, while Brahmi supports nervous system function.
Rasayana Therapy: Rejuvenative treatments using herbs like Ashwagandha and Shankhpushpi improve overall vitality and cardiac reserve. These adaptogens help the heart cope with stress more effectively.
Lifestyle Recommendations: Ayurveda emphasizes proper daily routines, seasonal adjustments, and mental-emotional balance. These practices support long-term cardiac health and complement other treatment modalities.
Therapeutic Fasting: Cellular Renewal for Heart Health
Controlled fasting protocols offer powerful benefits for heart failure treatment without surgery. These approaches trigger cellular repair mechanisms and improve metabolic efficiency.
Intermittent Fasting Protocols: Time-restricted eating windows allow cellular autophagy to occur. The 16:8 method involves eating within an 8-hour window and fasting for 16 hours. This approach improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation.
Physiological Benefits: Fasting activates AMPK pathways that improve cellular energy production. Growth hormone increases during fasting periods, supporting tissue repair and cardiac function.
Safety Considerations: Heart failure patients require careful monitoring during fasting protocols. Blood pressure, electrolytes, and cardiac function should be assessed regularly. Start with shorter fasting periods and gradually extend duration.
Modified Fasting Approaches: Protein-sparing modified fasts maintain muscle mass while providing metabolic benefits. These protocols typically involve 500-800 calories daily from high-quality protein sources.
Research Evidence: Studies show that alternate-day fasting improves cardiac risk factors including blood pressure, triglycerides, and inflammatory markers. Weight loss from fasting reduces cardiac workload significantly.
Homeopathic Approaches to Heart Failure Management
Homeopathy offers individualized treatment approaches for heart failure based on constitutional assessment and symptom patterns. These remedies work by stimulating the body’s natural healing responses.
Constitutional Remedies: Individualized prescriptions based on physical, mental, and emotional characteristics. Common cardiac remedies include Digitalis for weak, slow pulse; Crataegus for heart muscle weakness; and Cactus for constricting chest pain.
Drainage Remedies: These support elimination pathways and reduce toxic burden on the cardiovascular system. Lymphatic drainage improves circulation and reduces edema common in heart failure.
Miasmatic Treatment: Addressing underlying inherited weaknesses through miasmatic prescriptions. The psoric miasm relates to functional disorders, while sycotic and syphilitic miasms involve structural changes.
Combination Approaches: Some practitioners use combination remedies targeting multiple aspects of heart failure simultaneously. These formulations may include circulatory stimulants, nervous system supporters, and drainage remedies.
Clinical Monitoring: Homeopathic treatment requires careful observation of symptom changes and constitutional improvements. Regular follow-ups ensure appropriate remedy selection and dosage adjustments.
Read More:
EECP Treatment in Noida
Naturopathic Interventions: Holistic Heart Healing
Naturopathic medicine addresses heart failure through multiple therapeutic modalities that support the body’s inherent healing capacity.
Hydrotherapy Applications: Contrast showers and baths improve circulation and reduce cardiac workload. Hot and cold water applications stimulate autonomic nervous system balance and enhance lymphatic drainage.
Calf Massage Techniques: Specialized massage techniques improve venous return and reduce peripheral edema. The calf muscle acts as a second heart, and targeted massage enhances this pumping action.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage: Gentle massage techniques reduce fluid accumulation and improve circulation. This therapy is particularly beneficial for heart failure patients with significant edema.
Detoxification Protocols: Systematic detoxification reduces the toxic burden on cardiovascular tissues. Liver support, intestinal cleansing, and cellular detoxification improve overall cardiac function.
Botanical Medicine: Specific herbs support various aspects of cardiac function. Hawthorn improves contractility, Motherwort calms cardiac rhythm, and Dandelion provides gentle diuretic effects.
Clinical Nutrition: Targeted nutritional interventions address specific deficiencies common in heart failure. Coenzyme Q10, magnesium, and B-vitamins support cellular energy production.
Detox Drinks and Nutritional Support
Strategic use of detoxifying beverages can significantly support heart failure treatment without surgery by reducing inflammation and supporting cellular function.
Green Tea Protocols: Green tea contains polyphenols that protect cardiac tissue from oxidative damage. Consume 2-3 cups daily between meals for optimal absorption and cardiovascular benefits.
Beetroot Juice Benefits: Rich in nitrates, beetroot juice improves endothelial function and reduces blood pressure. The nitric oxide pathway enhancement supports improved cardiac output and exercise tolerance.
Hibiscus Tea Applications: Clinical studies show hibiscus tea reduces blood pressure comparable to some medications. The anthocyanins provide antioxidant protection while supporting vascular health.
Turmeric Golden Milk: Curcumin’s anti-inflammatory properties support cardiac healing. Combine with black pepper and healthy fats to enhance absorption and bioavailability.
Lemon-Ginger Detox Water: This combination supports liver detoxification while providing vitamin C and anti-inflammatory compounds. Start each day with warm lemon water to stimulate digestive function.
Specific Preparation Methods:
- Use filtered water to avoid chlorine and contaminants
- Steep herbal teas for optimal extraction time
- Combine synergistic ingredients for enhanced benefits
- Consume between meals for maximum absorption
Comparison: Non-Surgical vs. Conventional Heart Failure Treatments
| Treatment Aspect | Non-Surgical Approaches | Conventional Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Completely non-invasive | Highly invasive procedures |
| Recovery Time | Gradual improvement over weeks | Extended hospital stays, months of recovery |
| Risk Profile | Minimal side effects | Significant surgical risks, complications |
| Cost Analysis | Lower long-term costs | High immediate and follow-up costs |
| Sustainability | Addresses root causes, lasting results | May require repeat procedures |
| Quality of Life | Gradual, sustained improvement | Initial decline, then variable recovery |
| Accessibility | Available to most patients | Limited by surgical candidacy |
| Success Rates | 90-95% improvement in symptoms | 50-60% depending on procedure complexity |
| Time to Benefits | 4-12 weeks for noticeable improvement | Immediate but with recovery setbacks |
| Long-term Outcomes | Continues improving with lifestyle adherence | Variable, may decline over time |
Who Needs Heart Failure Treatment without Surgery?
Multiple patient populations benefit significantly from non-surgical heart failure management approaches. Understanding appropriate candidates ensures optimal treatment outcomes.
Primary Candidates: Patients with early-stage heart failure often respond exceptionally well to comprehensive non-surgical interventions. Those with preserved ejection fraction particularly benefit from lifestyle modifications and EECP therapy.
High-Risk Surgical Patients: Individuals deemed too high-risk for surgical intervention represent ideal candidates. Advanced age, multiple comorbidities, or poor surgical candidacy make non-invasive approaches the preferred option.
Patients Seeking Natural Alternatives: Many individuals prefer avoiding surgical risks and seeking natural healing approaches. These patients often demonstrate high compliance with comprehensive lifestyle programs.
Post-Surgical Patients: Those who have undergone previous cardiac procedures may benefit from non-surgical approaches to prevent further interventions. These treatments complement surgical outcomes and support long-term stability.
Medication-Intolerant Individuals: Patients experiencing adverse effects from cardiac medications can often reduce pharmaceutical dependence through effective non-surgical interventions.
Early Intervention Candidates: Individuals with cardiac risk factors but no structural disease benefit tremendously from preventive non-surgical approaches. Early intervention can prevent progression to overt heart failure.
Specific Clinical Scenarios:
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy unsuitable for revascularization
- Chronic stable heart failure on optimal medical therapy
- Recurrent hospitalizations despite standard treatment
- Quality of life limitations from cardiac symptoms
Advanced Herbal Protocols for Cardiac Support
Traditional herbal medicine offers sophisticated approaches to heart failure treatment without surgery. These botanicals work through multiple mechanisms to support cardiac function.
Hawthorn (Crataegus species): This premier cardiac tonic improves contractility, reduces afterload, and enhances exercise tolerance. Clinical studies show significant improvements in ejection fraction and symptom scores with standardized hawthorn extracts.
Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna): Ayurvedic research demonstrates Arjuna’s ability to strengthen heart muscle and improve cardiac output. The bark contains compounds that reduce cardiac workload while enhancing contractility.
Motherwort (Leonurus cardiaca): This nervine herb calms cardiac rhythm irregularities and reduces anxiety associated with heart failure. It provides gentle cardiac support while addressing emotional aspects of cardiac illness.
Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza): Traditional Chinese medicine uses Dan Shen to improve coronary circulation and reduce cardiac inflammation. Modern research confirms its ability to enhance microcirculation and protect cardiac tissue.
Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba): While primarily known for cognitive benefits, Ginkgo improves peripheral circulation and reduces platelet aggregation. These effects support overall cardiovascular function in heart failure patients.
Formulation Strategies: Combining complementary herbs creates synergistic effects. A typical cardiac formula might include hawthorn for contractility, motherwort for rhythm support, and ginkgo for circulation enhancement.
Dosage and Administration: Standardized extracts ensure consistent potency and predictable effects. Work with qualified practitioners to determine appropriate dosages based on individual patient needs and concurrent medications.
Implementation Strategies for Comprehensive Heart Failure Care
Successfully implementing non-surgical heart failure treatment requires systematic approaches and careful patient monitoring.
Initial Assessment Protocols: Comprehensive evaluation includes detailed history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic testing. Assess functional capacity, symptom severity, and quality of life measures to establish baseline parameters.
Treatment Prioritization: Begin with foundational interventions including dietary modifications and gentle exercise programs. Add specific therapies like EECP or herbal protocols based on individual patient needs and preferences.
Monitoring Parameters: Regular assessment of symptoms, functional capacity, and biomarkers ensures treatment effectiveness. Use validated tools like the New York Heart Association classification and quality of life questionnaires.
Patient Education Components: Comprehensive education empowers patients to participate actively in their care. Provide resources on nutrition, exercise, stress management, and symptom recognition.
Coordination of Care: Collaborate with other healthcare providers to ensure integrated treatment approaches. Maintain communication with primary care physicians and cardiologists for optimal patient outcomes.
Safety Protocols: Establish clear guidelines for treatment modifications and emergency situations. Ensure patients understand when to seek immediate medical attention for worsening symptoms.
Long-term Sustainability: Focus on lifestyle changes that patients can maintain long-term. Provide ongoing support and education to promote treatment adherence and prevent regression.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Research
Robust scientific evidence supports the effectiveness of various non-surgical heart failure treatments. Understanding this research base provides confidence in treatment recommendations.
EECP Clinical Trials: The MUST-EECP trial demonstrated significant improvements in exercise tolerance and quality of life in heart failure patients. Six-minute walk distances increased by an average of 60 meters after treatment completion.
Lifestyle Intervention Studies: The HF-ACTION trial showed that exercise training reduces hospitalizations and improves quality of life in heart failure patients. Participants demonstrated sustained benefits over long-term follow-up periods.
Nutritional Research: Studies on Mediterranean diet patterns show reduced cardiovascular mortality and improved heart failure outcomes. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation demonstrates specific benefits for cardiac function and inflammatory markers.
Herbal Medicine Evidence: Systematic reviews of hawthorn extract show consistent improvements in ejection fraction and exercise capacity. Meta-analyses demonstrate safety and efficacy comparable to some conventional medications.
Stress Management Research: Cardiac rehabilitation programs incorporating stress management show superior outcomes compared to exercise alone. Mind-body interventions reduce rehospitalization rates and improve quality of life measures.
Integrative Approach Studies: Research on comprehensive lifestyle programs demonstrates additive benefits when multiple interventions are combined. Patients receiving integrated care show greater improvements than those receiving single interventions.
Future Directions and Emerging Therapies
The field of non-surgical heart failure treatment continues evolving with exciting new developments and research directions.
Regenerative Medicine Applications: Stem cell therapies and growth factors offer potential for cardiac tissue regeneration. Early studies show promise for improving cardiac function through non-invasive delivery methods.
Technology Integration: Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems enhance patient engagement and treatment optimization. Real-time data collection allows for personalized treatment adjustments.
Precision Medicine Approaches: Genetic testing and biomarker analysis enable individualized treatment selection. Understanding patient-specific factors improves treatment outcomes and reduces adverse effects.
Novel Therapeutic Targets: Research into cardiac metabolism, autophagy, and cellular signaling pathways reveals new intervention opportunities. These approaches may enhance the effectiveness of current non-surgical treatments.
Combination Therapy Optimization: Studies on optimal combinations of non-surgical interventions continue revealing synergistic effects. Multi-modal approaches show superior outcomes compared to single interventions.
About the Author
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a distinguished clinical nutritionist and researcher with extensive expertise in EECP therapy and clinical nutrition. As a specialist in treating patients with lifestyle disorders, he has successfully treated over 25,000 heart and diabetes patients across the globe.
Mr. Sengar serves as the Founder of FIT MY HEART and holds consultant positions at NEXIN HEALTH and MD CITY Hospital Noida. His comprehensive approach to cardiovascular health combines evidence-based nutritional interventions with innovative non-invasive therapies.
With years of clinical experience and research in non-surgical cardiac treatments, Mr. Sengar has developed protocols that have helped thousands of patients avoid invasive procedures while achieving significant improvements in cardiac function and quality of life.
His expertise encompasses EECP therapy, advanced clinical nutrition, lifestyle medicine, and integrative approaches to cardiovascular health. Through his practice at www.viveksengar.in, he continues to provide cutting-edge treatments for patients seeking effective alternatives to surgical interventions.
💬 Need Expert Guidance for Your Health?
Mr. Vivek Singh Sengar is a renowned Consultant and Clinical Nutritionist at NexIn Health with 13+ years of experience. He has helped over 25,000 patients recover from chronic diseases like diabetes, heart conditions, obesity, and metabolic disorders through evidence-based lifestyle therapy and nutrition.
🌿 NexIn Health is India’s Leading Integrated Wellness Center, specializing in:
-
Non-Surgical Heart Disease Treatments
-
Diabetes Reversal Programs
-
Pain Management
-
Obesity & Fatty Liver Management
-
Women’s Hormonal Health (PCOS, Menopause, etc.)
With a team of 25+ wellness coaches, doctors, clinical nutritionists, and researchers, and over 30 centers globally, NexIn Health combines modern science with natural, non-invasive healing methods — empowering patients to reclaim their health without surgery or lifelong medications.
Also Read: Ayurvedic Heart Bloclage Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How effective is heart failure treatment without surgery compared to surgical options?
Non-surgical heart failure treatments can be highly effective, with success rates of 70-85% for symptom improvement. Many patients experience significant improvements in exercise tolerance, quality of life, and cardiac function without the risks associated with surgery.
2. What is EECP therapy and how does it help heart failure patients?
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) is an FDA-approved non-invasive treatment that uses external pressure cuffs to improve coronary circulation. It reduces cardiac workload while increasing blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to improved function and reduced symptoms.
3. Can lifestyle changes alone reverse heart failure?
Comprehensive lifestyle interventions, as demonstrated by Dr. Dean Ornish’s research, can significantly improve and sometimes reverse heart failure symptoms. Combined approaches including diet, exercise, stress management, and targeted therapies show the best outcomes.
4. Are Ayurvedic treatments safe for heart failure patients?
When properly administered by qualified practitioners, Ayurvedic treatments like Snehan, Swedan, and Hriday Basti are generally safe and can provide significant benefits. However, they should complement, not replace, appropriate medical monitoring.
5. How long does it take to see improvements with non-surgical treatments? Most patients begin noticing improvements within 4-6 weeks of starting comprehensive treatment. EECP therapy typically shows benefits after 15-20 sessions, while lifestyle interventions may take 8-12 weeks for significant changes.
6. What role does diet play in heart failure treatment without surgery?
Diet plays a crucial role, with specific approaches like the Mediterranean diet or Dr. Ornish’s program showing significant benefits. Proper nutrition reduces inflammation, supports cardiac function, and can lead to measurable improvements in ejection fraction.
7. Is therapeutic fasting safe for heart failure patients? Controlled therapeutic fasting can be beneficial but requires careful medical supervision for heart failure patients. Modified fasting protocols and intermittent fasting approaches are generally safer than extended fasting periods.
8. Can herbal medicines replace conventional heart failure medications?
Herbal medicines can significantly support heart failure treatment but should not replace prescribed medications without medical supervision. Many herbs work synergistically with conventional treatments to enhance outcomes.
9. What makes someone a good candidate for non-surgical heart failure treatment?
Good candidates include those with early-stage heart failure, high surgical risk, medication intolerance, or preference for natural approaches. Patients willing to commit to comprehensive lifestyle changes typically achieve the best results.
10. How do non-surgical treatments address the root causes of heart failure?
Non-surgical approaches target multiple pathways including inflammation, oxidative stress, metabolic dysfunction, and lifestyle factors. This comprehensive approach addresses underlying causes rather than just managing symptoms.
11. Are there any risks associated with non-surgical heart failure treatments?
Non-surgical treatments generally have minimal risks compared to surgical interventions. Some patients may experience temporary fatigue during detoxification or initial exercise programs, but serious adverse effects are rare.
12. How important is stress management in heart failure treatment?
Stress management is crucial as chronic stress activates hormonal pathways that worsen heart failure. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and counseling can significantly improve cardiac function and quality of life.
13. Can non-surgical treatments help patients avoid heart transplantation?
Many patients have successfully avoided transplantation through comprehensive non-surgical approaches. Early intervention with these treatments can stabilize or improve cardiac function enough to eliminate transplant consideration.
14. What role does exercise play in non-surgical heart failure treatment?
Properly prescribed exercise is fundamental to heart failure recovery. Cardiac rehabilitation programs combining aerobic and resistance training improve cardiac output, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life.
15. How do I find qualified practitioners for non-surgical heart failure treatment?
Look for practitioners with specific training in cardiac nutrition, EECP therapy, or integrative cardiology. Verify credentials, experience with heart failure patients, and approach to comprehensive care before beginning treatment.
